Browse by Subject
Results for Search : "303 Social processes"
|
|
Population ageing and social protection in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: With rapid increase in number of older persons, Malaysia is faced with multitude issues of graying population resulting from declining birth rate and rising life expectancy. In 2010 4.7% of the population was above 65 years old and the life expectancy was 71.7 years for males and 75 years for females. The New Economic Model for Malaysia (NEM) 2010 defines inclusiveness, high income and sustainability, as the three prong objective towards a developed nation in 2020. The underlying principle of the inclusiveness objective is to enable every Malaysian to have access to opportunities in order to contribute to the economy and to ensure that essential needs of the people are met. At least ten policy measures were recommended to improve the well being of the bottom 40% of the population, which has been identified as underserved. The question is, to what extent is the existing social safety net policy adequate to support every Malaysian to sustain a decent living? What are the issues and gaps with social safety net for older people? This paper attempts to answer these questions and to examine other related issues. It is divided into three parts: the first parts is an assessment of the existing social safety net in Malaysia; the second part looks at some case studies of NGO’s working with the older people and the final part offers some policy recommendations as a way forward.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing old age in a rapidly ageing high income city state: the case of Singapore
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Singapore, an affluent city state, is among the most rapidly ageing society globally. This is due to low fertility rate (TFR of 1.2 in 2011); and increasing life expectancy (18.3 years for men and 21.8 years for women at age 65 in 2011). Its support ratio (working age persons/elderly) is projected to decline from 7.9 in 2011 to 2.2 by 2030, representing a steep decline. It primarily relies on a mandatory savings tier to finance old age. This tier is administered by a statutory Board called Central Provident Fund (CPF) under the Ministry of Manpower. The CPF has over the years been used not just for retirement, but for housing health care, and other purposes. Its wide scope and mandate has resulted in considerable complexity. This paper provides an assessment of the extent to which the current old age financing arrangements are likely to address longevity, inflation, and survivors’ risks faced by individuals in their old age. Not only each person will need support for a longer period in old age, but societal and individual expectations about old age support are also changing, reflecting the affluent society.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social and economic aspects of elderly in Thailand
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Thailand is already an aging society. About 14% of population are elderly. Using a national survey, it can be shown that 16% of elderly households in the rural area have substandard living condition. The majority of elderly (60%) rely on remittance for their living. About 20% of elderly have to work for living and only 4% have government pension. Thailand is now organizing a National Saving Fund to promote saving for retirement. Another national survey finds that 80% of population want to save for their retirement but only 48% think that they can make regular monthly saving. This is consistent with another survey which finds that 50%-60% of elderly actually prepared themselves physically and mentally into the elder period. Elderly are less happy than the young. They are quite healthy, about 90% of those in the 65-74 age group can take care of themselves. It was quite normal in the Thai culture that children take care of their old parents. Above 80% of population expect that their children will take care of them physically, mentally, and financially when they become old. Taking care of old parents is something done by daughter. About 45% of elderly who are older than 94 years are taken care by daughter or daughter-in-law, another 38% take care of themselves. UN projects that Thailand will have 20 million elderly in the next 20 years which makes the elderly account for 26% of population or 45% of working age population. Without income security and long term care schemes for elderly, it would be very difficult for children to take care of their parents.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Home care for older people in ASEAN member countries
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: It is estimated that population of over 60 years in the South-Asia will triple between 2000 and 2050. By 2050, one out of four older people will be over the age of 80. This causes a growing need for welfare and health services for older people. However, the traditional family support system is under pressure due to the trend towards nuclear families, prevailing migration of children and increasing participation of women in the workforce. In most developing countries, the lack of appropriate programmes, policies and financing places further strain on an already stressed family system. In order to meet the growing needs of “CARE” services for older people in the community, HelpAge Korea have implemented HOME CARE project under the ROK-ASEAN Cooperation Project, which provides basic social and health related care services for older people who are poor and having difficulties of ADL at their home by volunteers. The HOME CARE project has been implemented in collaboration with government, non-government organizations and community people in 10 ASEAN member countries for 9 years from April 2003 to May 2012. The presentation shares the outcomes of HOME CARE project that has been successfully conducted in terms of developing localized model, strengthening GO & NGO collaboration for the expansion and influencing GO to integrate HOME CARE into policy framework. HOME CARE is one of community based care system to reduce the burden of the society and to improve the quality of life of older people. However, in responding to the need of vulnerable older people, there is no single solution but a series of care system is necessary. The presentation shares the future plan of ROK-ASEAN Cooperation Project on COMMUNITY BASED SERVICES of HelpAge Korea.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting the needs of older Malaysians: expansion, diversification, and multi-sector collaboration
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: The older population in Malaysia grew from 0.5 million in 1970 to almost 2.3 million in 2010, making up about 8% of the current total population. By 2020, one in ten Malaysians will be an older persons aged 60 years or over. Older Malaysians are a heterogeneous group with diverse demographic, socio-economic, cultural and religious characteristics. This paper assesses the adequacy, affordability, sustainability, equitability, predictability and robustness of current policies, programs and services to meet the needs of the ageing population in Malaysia. Based on the World Bank’s multipillar pension taxonomy, the analysis will focus on the social assistance scheme for the elderly (BOT), Pay-as-you-go financed state pension (JPA) and defined contribution funds (EPF). Between conditional cash transfers and mandatory retirement savings, the central role of informal support systems in old age has often been overlooked. Result from the past studies have shown that the family has played a central role in providing care and support for aged in Malaysia. A majority of older Malaysians still co-reside with their adult children and receives financial assistance from them. Older Malaysians today are living longer, better educated and wealthier and they will become consumers of a burgeoning silver industry. Balancing social and economic priorities in national development is a challenging task, but the two goals are not mutually exclusive. My topic focus on welfarism or paternalism will continue to render ageing populations as a dependent population, instead of empowering them. An inter-dependence approach, rooted in a mix of individual responsibility, family obligations, active civil society and state provisions (regulatory and non-regulatory), will enable a more broad-based and sustainable solution to meet the present and future needs of the elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bantuan sokongan dari wanita kepada ibubapa dan ibubapa mertua
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This study investigated ethnic diversity and other influencing factors among Malaysian women in Peninsular Malaysia in providing tangible support to their parents and parents-in-law. Data from the Women Sample of Malaysian Population and Family Survey (2004) was utilized. Tangible support was defined as either co-residing with parents (or in-laws), or financial/material transfers. Using logistic regression, we estimated the support to parents and parents-in-law separately. All possible pairwise interactions were tested using likelihood ratio test and Wald statistics, and significant interactions were added into each main effects model. Results revealed ethnic diversity in support. More offspring of women reduced support to parents only, while higher socioeconomic status of women increased support to both parents. Results also revealed that most divorcees co-resided with parents. Overall, most Malaysian women provide support to both sets of parents. Social policy should address opportunities for improving social mobility in women.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proses kaunseling keluarga di Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Family counseling is one of the interventions in family services for built a healthy family in Malaysia. This is a qualitative case study of a variety of 'settings' aims to explore the phenomenon of family counseling process conducted by practitioners in Malaysia with an in-depth interview technique, observation and document analysis. Study participants in the study were 12 family counseling practitioners from three counseling service centers. This study has five research questions namely to (i) identify the type of cases handled, number of cases and causes of problems in the family counseling process (ii) identify the initial relationship in the family counseling process (iii) explore the family counseling process (iv) identify approaches and skills used in family counseling and (v) explore the impetus and challenges of the family counseling process among family counseling practitioners in various settings in Malaysia. Cross -case analysis method based on interviews, observations and document analysis on family counseling practitioners was implemented using Nvivo 8 software. In this study, 190 themes and sub -themes were produced from 12 study participants. The results show that there are some similarities and differences between the family counseling process in Malaysia and the process framework in Western countries. These similarities and differences occur at all levels of the counseling process, skills, use of techniques, application of theory, and challenges in practice. The results of the study also show that the family counseling process among practitioners in Malaysia is tied to the education and training received by the practitioner, the context of religion, culture, values and SES of the family and community in Malaysia. Therefore, this study contributes to the provision of family counseling process that is very necessary in strengthening the family institution and can be an intervention in building a generation of excellent Malaysian society.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income security systems in the Republic of Korea? Directions for development
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: The four goals of public pensions - extension of coverage, provision of adequate benefits, an equitable share of costs between generations, and financial stability - are all important. However, as these four goals conflict and influence one another, it is difficult to attain them simultaneously. Therefore, it is necessary to compromise these goals at a certain level. National Pension in Korea has been developed within an astonishingly short period. However, coverage is still unsatisfactory and long-term financial state is unstable. These two issues seem to be the most urgent reform priorities. The former may be the most important issue because National Pension exists for the income security of people. Meanwhile, adequacy of benefit was partly relaxed through two reforms. Though long-term financial stability and equity between generations have been improved through some sacrifice of benefit level, these issues are still regarded as unresolved and need additional measures in Korea, one of the most rapidly ageing countries. In this paper, we examine the four major goals of National Pension, namely coverage, adequacy of benefit, inter-generational equity, and long-term financial stability. The coverage of the scheme should be extended and the average contribution period should be increased. Coverage must increase 10% by 2030 in terms of the ratio of old age pensioners to total old age people aged 65 and over. The benefit level of the National Pension may be targeted to 30% of average earnings in real term as of 2030. Other sources of old-age income can be from working, private pensions, and savings. For more stable finance and better equity between generations, we review four financial goals.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population aging in China: features, challenges & strategies
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Global response to population aging is confronted by a series of severe challenges, for example retirement and medical/caring costs adds to fiscal burdens, population aging withers the labor force, development and aging problems intermingle as growth of the aged population mostly takes place in developing countries and poverty of the aged remains an acute problem. All these issues may only be addressed when national governments all over the world take the needs of the aged into full consideration in developing their social policies, establish specific strategies for responding to population aging and incorporate such strategies into long-term national development frameworks. Population aging also reflects the progress and achievement that the human society has made in extending life expectancy, improving mother and child health and helping women realize family planning. Seniors are more than just beneficiaries of social welfare. As producers, consumers, spreaders of traditional cultures, care-takers of children in their families and communities, seniors also play positive irreplaceable roles. A shared goal for us all therefore is to regard aging as an achievement, respond to age-related issues with a positive, optimistic and rational altitude, view skills, experiences and resources of the elderly as capital of the social development course, incorporate aging into our development agendas, promote positive aging and thereby construct a sharing society regardless of age.
|
|
|
|
|
|
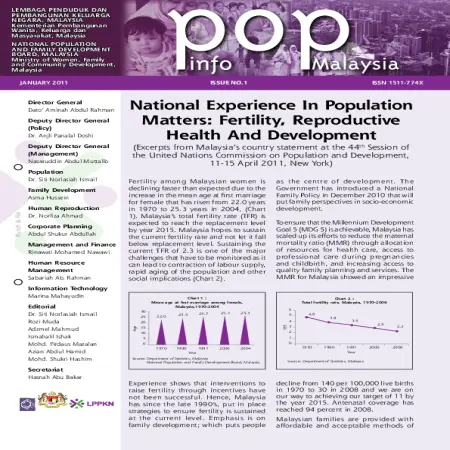
National experience in population matters : fertility, reproductive health and development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2011
Abstract: Fertility among Malaysian women is declining faster than expected due to the increase in the mean age at first marriage for female that has risen from 22.0 years in 1970 to 25.3 years in 2004. Malaysia’s total fertility rate (TFR) is expected to reach the replacement level by year 2015. Malaysia hopes to sustain the current fertility rate and not let it fall below replacement level.
|
|
|
|