Browse by Subject
Results for Search : "500 Natural Sciences and Mathemetics"
|
Mempertingkatkan komunikasi ibu bapa- remaja untuk menghalang tingkah laku seksual berisiko di kalangan remaja Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Year: 2024
Abstract: Parental communication with teenagers regarding reproductive and sexual health (SRH) remains minimal in Malaysia, with the topic being considered taboo and sensitive, rarely discussed openly within families. Teenagers are exposed to high-risk sexual activities, with 10-15% having...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of Sexting Intervention Module (SIM) using prototype willingness to sext among undergraduate students.
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Year: 2024
Abstract: Sexting exchanging sexually explicit messages (texts, images, videos) via online. High sexting prevalence was used to rationalized the need for intervention. Implication of sexting are correlated with cyberbullying, sexual risk behavior, and mental health issues. Objectives of this...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Situational analysis on family planning and reproductive health education in Malaysia and other selected Muslim countries Part I: needs analysis on family planning policy Part II: reproductive health education: policy and plan of action
Item Type: Research Report
Year: 2020
Abstract: This study is an initiative by the Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development (MWFCD) through the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) in collaboration with the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), who has been a strategic partner of NPFDB since the...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
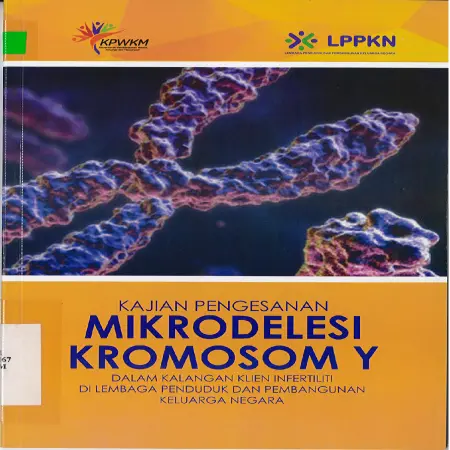
Kajian Pengesanan Mikrodelesi Kromosom Y dalam kalangan klien Infertiliti di Lembaga Penduduk dan Pembangunan Keluarga Negara
Item Type: Research Report
Year: 2017
Abstract: The study "Microdelesi of Y Chromosome among NPFDB Infertility Clients" conducted by the Biomedical Unit, NFPDB is to identify infertility factors from a genetic aspect. Study samples were obtained from infertility patients referred to the Cytogenetic Laboratory, NPFDB from 2003 to...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kajian perbandingan penggunaan tiga jenis rawatan hormon FSH dalam kalangan pesakit subfertiliti yang menjalani prosedur permanian beradas di Lembaga Penduduk dan Pembangunan Keluarga Negara
Item Type: Research Report
Year: 2017
Abstract: Since 1979, the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) has been providing subfertility management services to the public especially middle-income group. In line with the rapid pace of the latest technology and research developments, there are various types of...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertiliti dan Konsepsi - Senario memilih jantina
Item Type: Article
Year: 2016
Abstract: The tendency to choose the sex of a baby by a couple has occurred since time immemorial due to several factors including social, cultural, economic, belief, religious, and health factors. A study conducted by the United Nations Population Fund (UNPF) has outlined three main factors of...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memilih jantina bayi: bahagian 3
Item Type: Article
Year: 2016
Abstract: The tendency to choose the sex of the baby by the couple on several factors has been discussed in the previous article (part 1 and part 2) while in this part 3 shares about other methods in science that are also said to be a factor to the determination of the sex of the baby. Among...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|
|
A Study on health status of youth in Malaysia
Item Type: Research Report
Year: 2010
Abstract: This study analyzed health screening of 22,840 youths, who were distributed equally by ethnicity and camp sessions. Based on the analysis, 21.6% of youths were underweight, 18.1% pre-obese and 10.3% obese, with 0.3% perceived having body image disorders. With regards to sexual and...[Read More]
|
|
|
|
|