Browse by Author
Results for Family Name : "Azman" AND Given Name/Initial : "Nur Airena Aireen"
|
|
Active engagement and health status of older Malaysians evidence from a household survey
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 17/03/2023
Abstract: Malaysia is undergoing rapid age structural shift to becoming an ageing nation by 2030 when 14% of its population will be aged 60 and over. Population ageing strains the healthcare system due to the rapid rise in non-communicable diseases and poses enormous challenges in providing social protection.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correlates and consequences of delayed marriage in Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 01/10/2021
Abstract: This paper aims to examine the correlates of age at first marriage and the consequences of late marriage. Data for this paper were drawn from the 2014 Malaysian Population and Family Survey. Simple cross- tabulation and multiple classification analysis were used for the analysis. Age at marriage of women varied across socioeconomic groups.
|
|
|
|
|
|
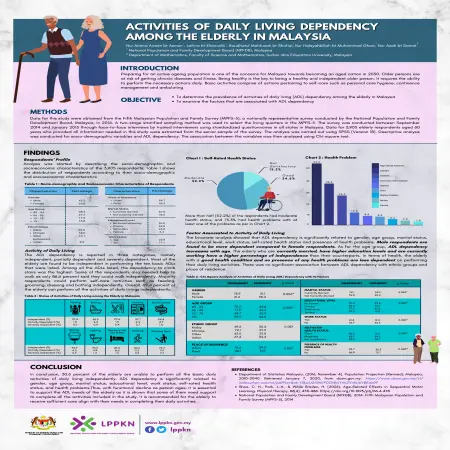
Activities of daily living dependency among the elderly in Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The objective of this study is to determine the prevalence of activities of daily living (ADL) dependency among the elderly in Malaysia and to examine the factors that are associated with ADL dependency.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insights into the well-being of dual earner families in Malaysia: findings from the Malaysian Family Well-Being Index Study 2019
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: Traditionally, GDP has been used as a measure of a country’s level of development, and the quality of life of citizens. Of late, the happiness index has gained increasing attention, as a measure of well-being, to include income distribution and non-financial aspects, such religious and spiritual well-being, and inter-personal relationship. Malaysia has conducted three rounds of the family well-being surveys to provide inputs for the five-year development plans. The overall family well-being score among dual earner families in Malaysia was 7.84 out of a maximum scale of 10, which is at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
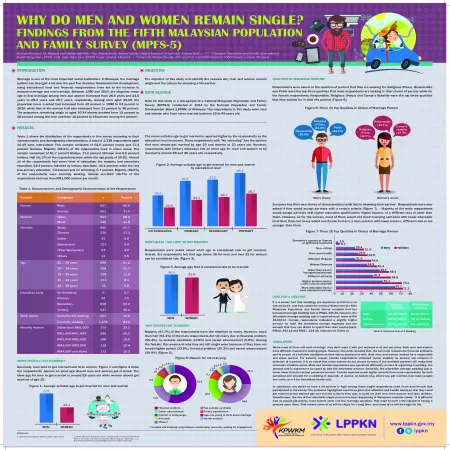
Why do men and women remain single? Findings from the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5)
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 01/07/2015
Abstract: Marriage is one of the most important social institutions. In Malaysia, the marriage pattern has changed a lot over the past few decades. Socioeconomic development, rising educational level and financial independence have led to the increase in delayed marriage and non-marriage. Between 1980 and 2010, the singulate mean age at first marriage among men and women increased from 26.6 years and 23.5 years to 28.0 years and 25.7 years, respectively. Among men aged 25-29, the proportion never married had increased from 40 percent in 1980 to 53 percent in 2010, while that of the women had also increased from 21 percent to 38 percent. The proportion remaining single at aged 30-34 almost doubled from 15 percent to 28 percent among the men and from 10 percent to 18 percent among the women. The objective of this study is to identify the reasons why men and women remain single and the criteria for choosing a life partner.
|
|
|
|
|
|
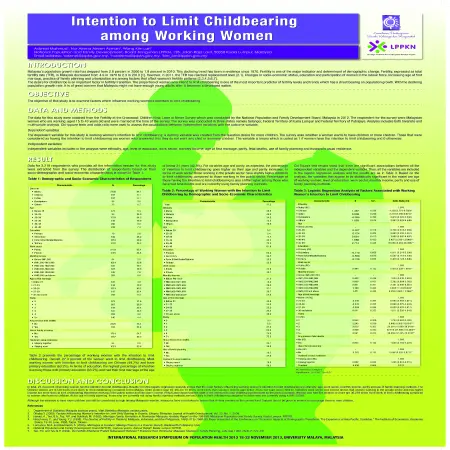
Intention to limit childbearing among working women
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2013
Abstract: Malaysia's population growth the rate has dropped from 2.6 percent in 2000 to 1.9 percent in 2010. This declining trends has been in evidence since 1970. Fertility is one of the major indicator and determinant of demographic change. Fertility, expressed as total fertility rate (TFR), in Malaysia decreased from 4.9 in 1970 to 2.3 in 2010. However, in 2011, the TFR has reached replacement level (2.1). Changes in socio-economic status, education and participation of women in the labour force, increasing age at first marriage, practice of family planning and urbanization are among factors that affect women's fertility pattern.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socio-economic determinants of pap smear screening among married women in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/02/2013
Abstract: This study is to identify the influences of socio-economic factors towards the practice of Pap smear screening among ever married women. Bivariate correlations and logistic regression analysis was applied to the data set containing 3,283 ever married women age 15-49 years, interviewed during the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2004. It was found that only half the women had undergone Pap smear screening prior three years of survey, in which Chinese had the highest percentage of Pap smear screening. The logistic statistical analysis also had identified several variables has important determinant has of Pap smear screening for ever married women. Finding from this study suggest a significant relationship between the cervical cancer awareness and knowledge, age and ethnicity for those women who practice Pap smear screening.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Migration in Malaysia: social and family impact
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This paper highlights the key findings from surveys done by the Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development (MWFCD) and the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB). The Survey on the Implications of Employing Foreign Domestic Helpers (FDH) on the Family Institution in Malaysia was conducted by the MWFCD in 2009. The study found that many families rely on FDH for child care and domestic work. Some of the families find that having a FDH has a negative effect on their family relationships while some have no problems with it. The study on Indonesian Migrants in Tawau, Sabah conducted by the NPFDB in 2010 found that the local community in Sabah felt that the presence of Indonesian migrants in their community had both positive and negative effects. The effects of migrants were studied from the perspective of economy, education, health, safety, culture, housing and neighbourhood.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The impact of Indonesian migrants from the locals' perception: a study in Sabah, Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/08/2012
Abstract: Being a developed country, Malaysia has been receiving a large number of labour migrants from other neighboring countries. Statistics show that the total number of non-Malaysians in 2010 is 2.3 million compared to 1.3 million in the year 2000. It is over 8 percent of the total population in Malaysia and comprises mostly of Indonesian migrants. This phenomena has a great impact on Malaysia and its people. The objective of this study is to determine the impact of Indonesian migrants from the locals' perception and also to determine if gender, ethnicity, religion, marital status, educational level, job industry and monthly income make a difference in their perception. The data used for this study were obtained from the Study on Indonesian Migrants in Tawau, Sabah conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) Malaysia in 2010. The survey managed to obtain information from 787 locals in Tawau. The dependent variable is the overall perception of the locals on the impact of the Indonesian migrants while the independent variables are gender, ethnicity, religion, marital status, educational level, job industry and monthly income. Independent t-test and analysis of variances (ANOVA) were applied to the data set. As a result, this study indicates that the locals in Tawau feel that the presence of the Indonesian migrants does have an effect on them. The mean score obtained was 95.053 out of a total of 135. The results of ANOVA showed that ethnicity (F = 6.950, df = 7), marital status (F = 12.320, df = 3), education level (F = 4.058, df = 7), job industry (F = 27.374, df = 3), and monthly income (F = 15.201, df = 6) contributed to the differences in the locals' perception on the impact of Indonesian migrants. Only gender and religion does not affect their perception. Thus, the entrance of Indonesian workers needs to be monitored as their presence are affecting the locals.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Keinginan kesuburan
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: The decline in fertility rates in Malaysia is happening rapidly and it is expected that the rate will reach the replacement level (replacement level = 2.1) in 2015. A woman's desire/decision to have a child has a direct impact on the fertility rate and population growth. Thus, the study aims to identify the factors that influence women's desire to have children or do not need to be implemented. Data and Methodology: This paper presents the preliminary findings of the study Fertility at the Crossroad: Children Now, Later or Never conducted by LPPKN in 2012. This study uses a cross -sectional survey design method with a focus on women in the reproductive age group. 15-49 years working in the public sector in Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya and Selangor. The method of data collection was through face -to -face interviews and self -administered using a questionnaire. Through stratified sampling method, a total of 98 public sector agencies were selected. To achieve the objectives of the study, the data obtained were analyzed using Descriptive Statistics, Chi Square and Logistic Regression (Forward LR Method). The dependent variable studied was the desire to have children (0 = do not want more children, 1 = want more children). While there are nine (9) independent variables studied namely age, ethnicity, education level, job grade (Management and Professional/Support), income, number of childbirths, pregnancy history (miscarriage/stillbirth/abortion), fertility problems and The husband lives far away. Findings: In total, a total of 1,898 data for women working in the public sector were analyzed. A total of 75.9% of respondents have a desire to have children. The results of Chi -Square analysis showed that the variables of age, ethnicity, income, number of births, pregnancy history, fertility problems and husbands living far apart had a significant relationship with the desire to have children. However, there is no evidence to suggest that post grade has a relationship with childbearing desire. Logistic regression test (Forward LR Method) showed that 57.8% of the variation in women's desire to have children can be explained by four independent variables, namely fertility problems, ethnicity, age and number of births. Conclusion: The results of the study found that women's desire to have children can be considered high. To support women's desire to have children, various forms of assistance/support should be provided by the employer/government. Among the main assistance/support needed are childcare centers at work, holiday facilities to care for sick children, subsidized childcare costs and full-paid facilities for children in need of special care.
|
|
|
|