Browse by Type
|
|
Fifty years of population ageing in Selangor: 1970-2020
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2024
Abstract: According to the 2020 Cencus, Selangor Darul Ehsan is the most populous States in Malaysia with total population of 6,994,423 persons and 1,836,410 households (average household size= 3.8 persons). With a total GDP of RM 326,805 million (RM 48,606 per capita), the relatively young State has a positive net migration rate although the absolute number of older persons has reached a staggering 714.4 thousand, or in other words, 21.4% of all older persons aged 60 years or over in Malaysia resides in Selangor.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faktor kritikal mendepani isu dan cabaran tenaga kerja menua
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: An aging workforce is one of the few phenomena faced by countries experiencing an aging population. This is also the case in Malaysia which has been categorized as an aging country by the World Bank since 2020. The aging workforce poses a number of issues and challenges to policy makers, employers and employees, especially those who are going through the aging process themselves.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faktor yang mempengaruhi amalan selamat pengurusan kebersihan haid dalam kalangan pelajar perempuan di Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Menstruation is a normal physiological process of females at their reproductive age and it requires the best regular hygiene management. However, unsafe menstrual hygienic practice can lead to problems related to reproductive health, poor educational performance and poor quality of life. This study aims to examine the level of safe practices and identify the factors that influence safe practices in the management of menstrual hygiene.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Factors affecting financial wellbeing among informal sector workers in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Challenges in the employment sector have become a global concern since the country was hit by the COVID-19 epidemic which caused a financial crisis, threatened the survival and wellbeing of the people and resulted in many individuals moving from the formal employment sector to the informal employment sector. The large size of the informal sector can hinder national development due to lower overall productivity, less tax revenue to the government, and lack of access to social safety nets and can lead to poverty, income inequality, and economic vulnerability.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family well being & the emergence of global pandemic
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) has introduced a Family Well-Being Index (FWBI) to specifically measure the well-being of families in Malaysia. The third series of the FWBI was conducted in 2019, prior to pandemic which start hitting the globe at the end of year. The FWBI 2019 reached a new highest score of 7.72 out of a maximum scale of 10. Although the FWBI 2019 score is still at a moderate level, it has shown an increase of 0.39 points compared to previous 7.33 for FWBI 2016. The FWBI 2019 score is a reflection of the family well-being in the country before COVID-19 pandemic began. Since then, every aspect of our life have been aff¬ected and subsequently transform the way we work and doing things. In addition to hampering the economy, the pandemic has also impacting family institution as a whole.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fatherhood program and children’s development: Does it mature?
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The prevalence of social problems and criminal cases among teenagers in Malaysia is at an alarming level. Often, such problems are associated with the fragility of the family institution underpinned by the role of the father. In Malaysia, fatherhood-related programs are still limited and minimal compared to the United States where most initiatives to support fathers have been implemented through father-specific programs designed to improve fathers' economic self-sufficiency, parenting knowledge and skills.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertility preferences in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 30/11/2018
Abstract: Most countries have been experiencing changes in fertility pattern over the last few decades. Fertility transition from high to low is a relatively recent phenomenon in Malaysia. The total fertility rate (TFR) had declined from 4.9 children per woman in 1970 to 4.0 in 1980. It has continued to fall and has reached the replacement level of 2.1 in 2010. This chapter provides the trend analysis and a comparative analysis of fertility trends to explain the fertility transition of Malaysia’s population. Data used in this study were obtained from Department of Statistics, Malaysia and Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2014. The result of this study showed that the fertility rate between age groups was higher among Malay than other ethnics since 1991–2010. Across all ages, the fertility rate has a negative correlation with the educational level where women with tertiary education tend to have fewer children compared to less educated women. This study also presents the fertility desire in Malaysia. There is a negative correlation between age group and fertility desire. In addition, the desire to stop childbearing is found to be stronger when women have had three living children. The findings of this study will help policy makers to plan programmes to improve the fertility rate in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
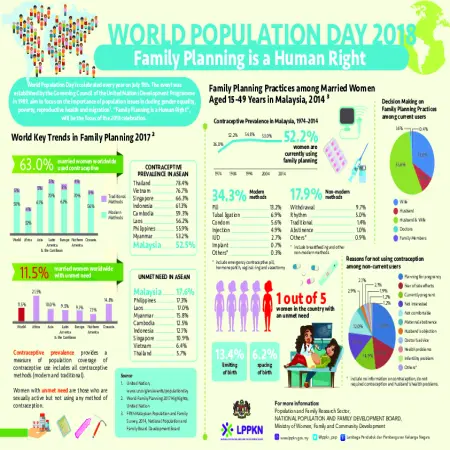
Family planning is a human right
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2018
Abstract: World Population Day is celebrated every year on July 11th. The event was established by the Governing Council of the United Nations Development Programme in 1989, aim to focus on the importance of population issues including gender equality, poverty, reproductive health and migration. Family Planning is a Human Right, will be the focus of the 2018 celebration.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fathers' bonding and self-esteem among trainees in the drugs treatment and rehabilitation center in Melaka
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2018
Abstract: The paper discusses a survey study that examined the father’s bonding and its relationship with self-esteem. A total of 97 trainees in Cure and Care Rehabilitation Centre (CCRC), Tiang Dua, Melaka who participated in the study had responded to questionnaires on aspects of fathers’ bonding and their self-esteem. Analysis of correlation between fathers’ bonding and self-esteem were performed. Frequency count, percentage and mean were also calculated to examine the parenting involvement among fathers. The Pearson r Value, the significant and t-Test were used to the objectives of the study. Results indicated that 65% have lower bonding with their father’s whereas only 35% have had a high father’s bonding. The t-test also showed there is non significant correlation in the index of father’s bonding with self-esteem (Sig=.402 and r value= -0.086). However, the respondents felt that their fathers were unfriendly and had little communication with them. The correlation between fathers’ bonding and their self-esteem was rather low. This implies that the roles of father in parenting need to be examined further.
|
|
|
|