TOPICS
Results for Topics : "Ageing"
Article (5)
|
|
Active engagement and health status of older Malaysians evidence from a household survey
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 17/03/2023
Abstract: Malaysia is undergoing rapid age structural shift to becoming an ageing nation by 2030 when 14% of its population will be aged 60 and over. Population ageing strains the healthcare system due to the rapid rise in non-communicable diseases and poses enormous challenges in providing social protection.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program dan aktiviti warga emas satu kajian di pusat aktiviti warga emas (PAWE) Negeri Kedah
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2021
Abstract: For the State of Kedah, the aging status based on statistics up to now is 12.6% of the elderly population based on the total population in the State of Kedah of 2.2 million people. In accordance with the wishes of the Federal Government, it is necessary to establish every PAWE in every Parliament to draft and enable the elderly to always be active in the State of Kedah. In the State of Kedah there are 12 PAWEs representing 12 Parliamentary constituencies and this study will look at the involvement of the elderly in activities and programs that successfully attract their interests and tendencies. At the end of the study, the researcher will state the need for such a program as an example among the elderly and be used as a guide in the future.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Regulating retirement village in Malaysia; the way forward
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2021
Abstract: As Malaysia is predicted to be an ageing nation by the year 2030, developing a retirement village shall be an avenue for senior citizens to have a welfare and conducive placement for them to spend their time with value-added amenities that cater their special needs. This paper discusses the overview concept and elements of retirement village sector in Malaysia and other jurisdictions, and the possibility of having a sustainable legal framework in regulating the sector. The legal issues and possible unintended consequences that may arise out of the development of retirement village in Malaysia is also discussed in this paper.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gaya hidup wanita dan faktor risiko kanser payudara: satu kajian literatur
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breast cancer is currently the most common cancer in women worldwide. It is said that there is no proven method of preventing cancer. However, studies have shown that there are some women’s lifestyle factors that have been scientifically shown to increase the risk of breast cancer. A review of the literature from the epidemiological, medical, and psychosocial disciplines strives to analyse factors that tend to increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Published material reviewed concerning the connection between breast cancer risk and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. This review shows that several women’s
lifestyle factors have been regularly considered as risk factors for developing breast cancer. They include women who have not had children or women who had their first child at an older age, short duration of brestfeeding or not breastfeed at all, diet and nutrition, and psychological stress.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socioeconomic status of older Malaysians: a gender comparison
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2004
Abstract: The feminization of old age is a global phenomenon that brings with it unique and multiple challenges. Cumulative effects of past (and present) gender inequality only further compound the difficulties older women face in later life.The objective of this paper is to provide a comparison of the socioeconomic status between older men and women. A survey of the older population living in the community was conducted from 22nd October till 8th December 1999.The sample was derived from stratified district (rural and urban) of 4 states (Johor, Perak, Kedah, Kelantan) where 1726 older persons were successfully interviewed. Out of that sample, 843 are women. Results from the study showed that there is significant difference between older men and women in terms of monthly income(t=-3.567,p<0.01). The primary source of sustenance for older women actually comes from their adults sons (M=168.3, SD=207.8)and daughters (M=133.4,SD=190.3). The value of monetary assistance from sons increases when the female elderly have more children (r=0.123,p<0.01). There is also significant relationship between gender and other socioeconomic indicators such as employment, past occupation, education, marital status and home ownership. In conclusion, women face a greater risk in the future of a greying population as they form the major stakeholders. Being financially beholden to their adult children, older Malaysian women's dependency is an important issue that requires attention. Further investigation is needed to determine if the gender differences will translate or relate to other variables such as health and overall well being.
|
|
|
|
Book (2)
|
|
Prosiding Persidangan Kependudukan Kebangsaan 2023 (PERKKS 23): “Penduduk dan Keluarga Mampan, Membangun Malaysia MADANI”
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2024
Abstract: Collection of papers presented during the 2023 National Population Conference (PERKKS 23), 21-22 November 2023, Pulse Grande Hotel, Putrajaya.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prosiding Persidangan Kependudukan Kebangsaan 2022 (PERKKS 22): “Pemerkasaan Penduduk dan Keluarga, Teras Negara Maju”
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2022
Abstract: Collection of papers presented during the 2022 National Population Conference (PERKKS 22), 10-11 November 2022, Bangi Resort Hotel, Selangor.
|
|
|
|
Book Section (6)
|
|
Faktor kritikal mendepani isu dan cabaran tenaga kerja menua
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2024
Abstract: An aging workforce is one of the few phenomena faced by countries experiencing an aging population. This is also the case in Malaysia which has been categorized as an aging country by the World Bank since 2020. The aging workforce poses a number of issues and challenges to policy makers, employers and employees, especially those who are going through the aging process themselves.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bandar pintar inklusif warga emas: Bagaimana ketersediaan kita?
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 01/07/2022
Abstract: The Third National Physical Plan projects that about 77% of Malaysia’s population will live in cities in 2020 and is expected to increase to 82% by 2030 and 87% by 2050. The elderly in Malaysia (those aged 60 and above) will increase from a total of 2,875 in 2015, to 5,196 million in 2030 and 9,593 in 2050. Malaysia as a developing country will experience an ageing population in the near future.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The impact of ageing, population growth and fertility rate on economic growth: new evidence using dynamic heterogeneous panel
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2022
Abstract: Over the last century, a declining fertility and mortality rate have led to an ageing population. This trend was primarily found in Europe and North America prior to the past two decades, but it has since become widespread. Due to altered reproduction patterns and rising life expectancy, the ageing population will probably increase.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term care insurance (LTCI) for the ageing society in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2022
Abstract: The increase in life expectancy and declining fertility rates have contributed to the rising tide of the ageing population in Malaysia. Undeniably, an ageing population poses the need for policy changes to address the economic and social risks caused. Against this backdrop, it is therefore crucial for Malaysia to give serious attention in developing a policy related to long-term care financing.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tahap kesejahteraan penduduk warga tua: kajian kes warga tua Bandar Baru Sungai Buloh
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2022
Abstract: By 2030, Malaysia is projected by the United Nations to reach the ageing country status with 15 percent of the country’s population aged 60 and above. This aging phenomenon is seen to cause a great impact and challenge to the development of the country. Approriate planning is needed to deal with this phenomenon and ensure the well-being of the elderly. This study was conducted to identify the elements of the well-being of the elderly and their level of well-being by making Bandar Baru Sungai Buloh as the study area.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The impact of aging and fertility rate on economic growth in Malaysia: new evidence using ARDL model
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: Population aging and the health status of the community are the primary agenda in the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals 2030 (SDG, 2030). However, current trends in the world have shown a rapid increase in the aging population rate, whereas the birth rate has shown a downward trend. Malaysia is no exception in this regard, which is expected to become an old country status by 2030 when the population aged 60 years and above reaches 15% of the total population.
|
|
|
|
Conference or Workshop Item (18)
|
|
Determinants of loneliness among elderly in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2016
Abstract: As of 2014, there is an estimated of 2.7 million elderly in Malaysia or 8.9% out of the total population of 30.3 million. Recent projections estimated that Malaysia will become an ageing nation by 2035 when 15% of the population falls into this group. As the number of the elderly population continues to grow, loneliness is becoming one of the major issues leading to impaired quality of life among elderly. Loneliness might lead to mental problems and stress among the elderly. This study attempts to examine the characteristics and influencing factors of loneliness among elderly in Malaysia. Data for this study is a sub-sample of a bigger national study gathered through the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5) conducted in 2014 by the National Population and Family Development Board Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loneliness among older Malaysians
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: Loneliness is a prevalent issue among older persons and it is an important indicator of their subjective well-being. Persistent loneliness or extreme cases of loneliness may lead to higher risks of psychological disorder, mental health problems, depression or suicide. Family support is a great importance in determining the quality of life and well-being of older persons. The objective of this study is to examine factors influencing the feeling of loneliness among older Malaysians. We hypothesize that loneliness among older persons varies according to their socio-demographic characteristics and is affected by their health and physical condition and community participation as well as the various forms of family support.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social pension, aging and poverty in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: The increasing number of elderly in Malaysia calls for a more stringent policy to safeguard the well-being of the elderly. The old age protection such as the pension scheme, Employees Provident Fund and the old age cash assistance although in tact, deemed to be inadequate to eradicate elderly poverty. One possible solution to secure financial protection during old age is through social pension that provides non-labor income for the retirees or elderly with the purpose of preventing or reducing elderly poverty. This paper attempts to estimate the financial cost of social pension scheme and quantify its potential role in reducing elderly poverty in Malaysia. The financial cost of social pension scheme was calculated as a percentage to GDP. By using the 2009 household income expenditure survey, the paper estimated the potential roles of social pension in eradicating elderly poverty. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the cost social pension could be kept at an average of 1.30 percentage of GDP. The 2009 HIES data also indicated that poverty could be eventually be eradicated with social pension while cost of the social pension was kept at reasonable levels.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pendekatan sokongan keluarga dalam kalangan penjaga warga tua: pengetahuan, kemahiran dan kesejahteraan
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study is conducted in line with global development (modernization) the impact on the care of elderly parents in their own (informal) families is declining and may worsen in the future. This phenomenon does not only occur in Malaysia but it is a global issue especially in developed and developing countries. Among the causes of this phenomenon are due to the increase in life expectancy of elderly parents (Department of Statistics Malaysia, 2000), the effects of modernization and changes in family structure, increase in divorce rates, reduction in birth rates, geographical movements and globalization.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family well being: enhancing National Policies towards elderly parents
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Malaysia will be aged by the year 2030. The objective of National Policy for Older Persons, 2011 is to enhance the respect for and self-worth of the elderly in family, society and nation, to develop the potential of the elderly so that they remain active and productive in national development and to create opportunities for them to continue to live independently and to encourage the establishment and the provision of specific facilities to ensure the care and protection of the elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kesan amalan dan status kesihatan terhadap kemurungan di kalangan warga tua lelaki di Semenanjung Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This study aims to look at the factors of practice and health status that contribute to depression among elderly men aged 60 years and above in Peninsular Malaysia. The data used in this study was obtained from the 4th Malaysian Population and Family Survey which was conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (LPPKN). The data obtained were analyzed using Descriptive Statistics and Logistic Regression. Among the variables used were the level of health, frequency of treatment, disease, frequency of exercise and health check-ups. The results of the analysis showed that coronary heart disease, decreased labor capacity, restless inability to sleep and attending religious ceremonies were independent variables influencing the risk of depression.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing old age in a rapidly ageing high income city state: the case of Singapore
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Singapore, an affluent city state, is among the most rapidly ageing society globally. This is due to low fertility rate (TFR of 1.2 in 2011); and increasing life expectancy (18.3 years for men and 21.8 years for women at age 65 in 2011). Its support ratio (working age persons/elderly) is projected to decline from 7.9 in 2011 to 2.2 by 2030, representing a steep decline. It primarily relies on a mandatory savings tier to finance old age. This tier is administered by a statutory Board called Central Provident Fund (CPF) under the Ministry of Manpower. The CPF has over the years been used not just for retirement, but for housing health care, and other purposes. Its wide scope and mandate has resulted in considerable complexity. This paper provides an assessment of the extent to which the current old age financing arrangements are likely to address longevity, inflation, and survivors’ risks faced by individuals in their old age. Not only each person will need support for a longer period in old age, but societal and individual expectations about old age support are also changing, reflecting the affluent society.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enhancing family institution towards addressing population ageing
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Malaysia will be aged by the year 2030. The objective of National Policy for Older Persons, 2011 is to enhance the respect for and self-worth of the elderly in family, society and nation at the same time to develop the potential of the elderly so that they remain active and productive in national development and to create opportunities for them to continue to live independently and to encourage the establishment and the provision of specific facilities to ensure the care and protection of the elderly. The areas of Plan of Action: Promotion and Advocacy, Lifelong Learning, Safety and Protection, Governance and Shared Reasonability, Involvement and Intergenerational Solidarity, Research and Development.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social and economic aspects of elderly in Thailand
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Thailand is already an aging society. About 14% of population are elderly. Using a national survey, it can be shown that 16% of elderly households in the rural area have substandard living condition. The majority of elderly (60%) rely on remittance for their living. About 20% of elderly have to work for living and only 4% have government pension. Thailand is now organizing a National Saving Fund to promote saving for retirement. Another national survey finds that 80% of population want to save for their retirement but only 48% think that they can make regular monthly saving. This is consistent with another survey which finds that 50%-60% of elderly actually prepared themselves physically and mentally into the elder period. Elderly are less happy than the young. They are quite healthy, about 90% of those in the 65-74 age group can take care of themselves. It was quite normal in the Thai culture that children take care of their old parents. Above 80% of population expect that their children will take care of them physically, mentally, and financially when they become old. Taking care of old parents is something done by daughter. About 45% of elderly who are older than 94 years are taken care by daughter or daughter-in-law, another 38% take care of themselves. UN projects that Thailand will have 20 million elderly in the next 20 years which makes the elderly account for 26% of population or 45% of working age population. Without income security and long term care schemes for elderly, it would be very difficult for children to take care of their parents.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Productive aging - role of NGO
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Butler and Gleason (1985) define productive ageing as “the capacity of an individual or a population to serve in the paid workforce, to serve in volunteer activities, to assist in the family and to maintain himself or herself as independent as possible.” USIAMAS is a non-governmental organization (NGO), registered in 2002 with the Registrar of Societies. It is a non-profit and welfare related organization whose members are senior citizens themselves. USIAMAS was formed with the objectives of being a smart partner or consultant to government, corporate and other volunteer bodies who share the same mission and vision of planning, implementing, coordinating, evaluating policies, projects and programs for the wellbeing of senior citizens towards quality and meaningful life. Among the various programs run by USIAMAS to support productive ageing are seminars, capacity training programs for volunteers and with the cooperation of the Social Welfare Department of Malaysia manages an Activity Center for Senior Citizens in Kompleks Penyayang Sungai Buloh. USIAMAS was honored to be chosen by HELPAGE Korea to implement a pilot project on home-help in 2005. Home-help is a community support program aimed at ‘recruiting, developing and deploying volunteers to make regular visits as informal companions and soft-skilled caregivers to older persons staying in their homes.’The normal duties of a volunteer in a home-help program include ‘personal grooming, running errands, feeding, reminders on medication, writing letters, accompanying them on recreational activities, visit to hospitals, banks or supermarkets’ More often the mere art of listening and responding to the needs of older persons will help to overcome their feelings of ‘rejection, isolation, boredom and loneliness’. The pilot project which commenced in 2005 has now been extended to Negeri Sembilan and Melaka with the support of the Social Welfare Department of Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Philippine pension system: promoting fairness and sustainability
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This paper presentation about sharing knowledge on the retirement system in the Phillippines, currently characterized by a four-pillar structure. The first pillar refers to social assistance programs created to address the needs of the elderly poor. The second pillar covers the following mandatory defined-benefit programs: (i) the Social Security System (SSS) for private sector workers, (ii) the Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) for public sector workers, and (iii) the Armed Forces of the Philippines Retirement Service Benefit System for the military, which altogether cover about 79% of the labor force. The third pillar encompasses mandatory defined contribution programs, which can be further expanded. The fourth and final pillar covers voluntary pension programs, involving various forms of savings instrument. Because the pension system is fragmented, contributions and benefits vary depending on the program.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social protection for the older people in Vietnam: challenges and reform options
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This paper aims to argue that the Vietnamese population has been aging more quickly than expected, and as such policies toward an aging population, particularly delivery of social protection services for the aged, should be well-prepared from now in order to have older and wealthier population in the coming decades. The paper shows that the social protection schemes in Viet Nam, especially pensions and social allowances, have expanded and reached various groups of old-age persons and played an important role in reducing old-age poverty. Yet, there have remained a number of challenges that will substantially influence the current system in term of financial sustainability and generational equity. For the pension scheme, the paper argues that the current setting will not be financially stable and generational equity and as such it should be transformed toward a new setting. For the social allowances, a universal cash transfer program for older people would be influential and cost-saving in terms of poverty reduction.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Home care for older people in ASEAN member countries
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: It is estimated that population of over 60 years in the South-Asia will triple between 2000 and 2050. By 2050, one out of four older people will be over the age of 80. This causes a growing need for welfare and health services for older people. However, the traditional family support system is under pressure due to the trend towards nuclear families, prevailing migration of children and increasing participation of women in the workforce. In most developing countries, the lack of appropriate programmes, policies and financing places further strain on an already stressed family system. In order to meet the growing needs of “CARE” services for older people in the community, HelpAge Korea have implemented HOME CARE project under the ROK-ASEAN Cooperation Project, which provides basic social and health related care services for older people who are poor and having difficulties of ADL at their home by volunteers. The HOME CARE project has been implemented in collaboration with government, non-government organizations and community people in 10 ASEAN member countries for 9 years from April 2003 to May 2012. The presentation shares the outcomes of HOME CARE project that has been successfully conducted in terms of developing localized model, strengthening GO & NGO collaboration for the expansion and influencing GO to integrate HOME CARE into policy framework. HOME CARE is one of community based care system to reduce the burden of the society and to improve the quality of life of older people. However, in responding to the need of vulnerable older people, there is no single solution but a series of care system is necessary. The presentation shares the future plan of ROK-ASEAN Cooperation Project on COMMUNITY BASED SERVICES of HelpAge Korea.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting the needs of older Malaysians: expansion, diversification, and multi-sector collaboration
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: The older population in Malaysia grew from 0.5 million in 1970 to almost 2.3 million in 2010, making up about 8% of the current total population. By 2020, one in ten Malaysians will be an older persons aged 60 years or over. Older Malaysians are a heterogeneous group with diverse demographic, socio-economic, cultural and religious characteristics. This paper assesses the adequacy, affordability, sustainability, equitability, predictability and robustness of current policies, programs and services to meet the needs of the ageing population in Malaysia. Based on the World Bank’s multipillar pension taxonomy, the analysis will focus on the social assistance scheme for the elderly (BOT), Pay-as-you-go financed state pension (JPA) and defined contribution funds (EPF). Between conditional cash transfers and mandatory retirement savings, the central role of informal support systems in old age has often been overlooked. Result from the past studies have shown that the family has played a central role in providing care and support for aged in Malaysia. A majority of older Malaysians still co-reside with their adult children and receives financial assistance from them. Older Malaysians today are living longer, better educated and wealthier and they will become consumers of a burgeoning silver industry. Balancing social and economic priorities in national development is a challenging task, but the two goals are not mutually exclusive. My topic focus on welfarism or paternalism will continue to render ageing populations as a dependent population, instead of empowering them. An inter-dependence approach, rooted in a mix of individual responsibility, family obligations, active civil society and state provisions (regulatory and non-regulatory), will enable a more broad-based and sustainable solution to meet the present and future needs of the elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retirement planning: Dynamic and holistic approach in bridging the gaps and mitigating the risks
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Most of us will one day row old and frail. Some will be fortunate enough to be endowed with wealth and good health in retirement years. But others in fact many of us, some call it the 99% group, will not be so fortune. We may have wealth but not health. We may be healthy but not wealthy. Many will probably have enough income to put food and drink on the table, and roof over the head, but will there be enough to cover unexpected expenses? Can we depend on our children to financially and/or physically take care of us in our golden years? They too will likely be facing similar problems such as soaring costs of housing, children’s education, lifestyle upgrading, busy schedule and others making it less likely that we can depend on them for assistance. This paper discusses the needs as we age, identifies gaps that may occur and suggests the best ways for us to share and meet needs as individuals and as a nation. Retirement planning is dynamic and holistic. We are not just planning to build up wealth and good health, we must also plan to protect our wealth and health. When planning for retirement, all risks that we might face must be understood at the outset and strategies to mitigate them must be worked out.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population aging in China: features, challenges & strategies
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Global response to population aging is confronted by a series of severe challenges, for example retirement and medical/caring costs adds to fiscal burdens, population aging withers the labor force, development and aging problems intermingle as growth of the aged population mostly takes place in developing countries and poverty of the aged remains an acute problem. All these issues may only be addressed when national governments all over the world take the needs of the aged into full consideration in developing their social policies, establish specific strategies for responding to population aging and incorporate such strategies into long-term national development frameworks. Population aging also reflects the progress and achievement that the human society has made in extending life expectancy, improving mother and child health and helping women realize family planning. Seniors are more than just beneficiaries of social welfare. As producers, consumers, spreaders of traditional cultures, care-takers of children in their families and communities, seniors also play positive irreplaceable roles. A shared goal for us all therefore is to regard aging as an achievement, respond to age-related issues with a positive, optimistic and rational altitude, view skills, experiences and resources of the elderly as capital of the social development course, incorporate aging into our development agendas, promote positive aging and thereby construct a sharing society regardless of age.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertility transition in Asia in relation to family and population aging
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2006
Abstract: Declining fertility and increasing longevity have brought about remarkable shifts in the age structure of the population. Europe, Northern America and Australia/New Zealand initially experienced one of such inevitable demographic events, that is population aging. While the transition from the young-age population to the aging population occurred over a much longer period in the West, the speed of aging is much faster in low-fertility countries of Asia. This has now emerged as a new issue challenging many low-fertility countries in Asia, as it has implications for the family and caring for the older persons. This paper provides a general overview of the fertility transition in Asia and factors affecting the fertility decline. Focusing on low-fertility countries in Asia, the paper highlights the implications of low fertility on population aging. Various indicators of population aging, such as the changes in age structure, potential support ratio and feminization of the elderly population, are presented for a better understanding of the overall situation. Comparisons are made with Europe, Northern America and Australia/New Zealand to put forward the magnitude of the challenge. As the Asian region contains over 60 percents of the global population and has experienced a rapid decline in fertility, the absolute size of the older population is a major concern. While the overall population growth rate has been declining over time, the number of older persons is increasing at a rate at least twice as high. In addition to the increase in older persons, a gender disparity in the improvements in the life expectancy at birth is likely to be illiterate and living in poverty. Providing family support, health care and financial security are some of the contentious issues aging societies will face. There have been discussions concerning the possibility of increasing fertility in countries with below replacement fertility. It is, therefore, crucial for governments to plan for an aging society long before fertility reaches a very low level. Meanwhile, it is important for Asian countries to recognize the significance of aging problems and start formulating policies for the elderly given that it takes several decades for government old-age pension insurance schemes to mature and operate at full scale. It would be more difficult for families to care for their older members because families would be smaller, people would live longer and the migration of young adults would mean that families would fragment. the present trends present a major challenge to address the needs of families. It is, therefore, important to consider the present trends in designing social policies, put the family at the centre of any future social policy development and examine good national practices when designing a new approach to family policies.
|
|
|
|
Infographic (4)
|
|
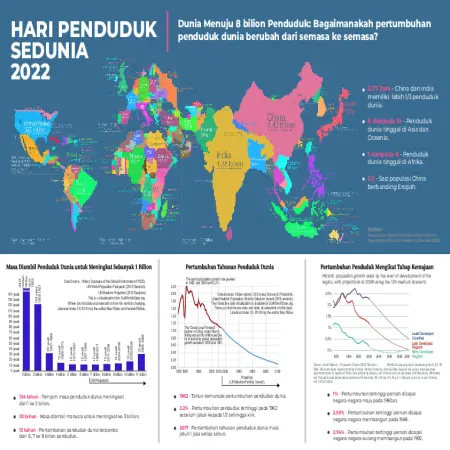
Penurunan Kadar Kesuburan Di Malaysia
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/10/2023
Abstract: Total Fertility rate (TFR) is a demographic indicator used to estimate the average number of children a woman should give birth to during her reproductive period. The findings of a poll in Sarawak found that the total TFR for the state of Sarawak is decreasing drastically. 12.6% of couples have had or are experiencing fertility problems and it is difficult to conceive within a year after marriage.
|
|
|
|
|
|
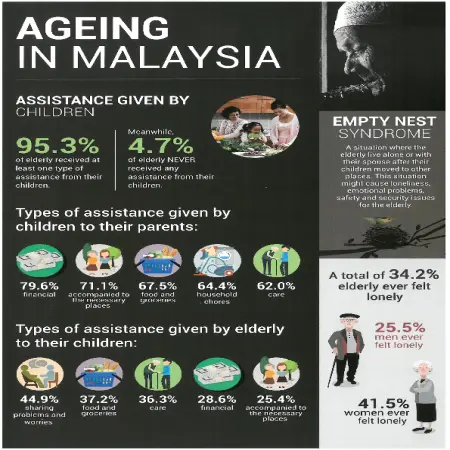
Malaysia negara tua 2030
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2018
Abstract: This infographic shows about the main factors and challenges of aging in Malaysia. According to the United Nations (UN) definition, senior citizens are among those aged 60 and above. This definition was introduced during the “World Assembly on Aging” held in Vienna in 1982. In recognition of the elderly, the UN through Resolution No. 45/106 has also declared October 1 as International Senior Citizens Day. In Malaysia, the National Senior Citizens Day celebration has been celebrated on October 1 every year since 1992.
|
|
|
|
Newsletter (8)
|
|
Malaysia's demographic dividend: harnessing the first and the second
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: In 2020, Malaysia's economy was one of the largest in Southeast Asia, boasting a population of 32.4 million. As a relatively young country, Malaysia has undergone significant improvements in education and healthcare facilities over the last few decades, leading to rapidly changing demographics. These changes in the population structure will open windows of opportunity to harness the first and second demographic dividends.
|
|
|
|
|
|
General debate on review and appraisal of the programme of action of the International Conference on Population Development and its contribution to the follow - up and review of the 2030 agenda for sustainable development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2019
Abstract: The Population of Malaysia is estimated at 33 million today with 3.1 million are non-citizens. The rate of population growth has declined to 1.7 per cent per annum from about 2.5 per cent during the 1970-2000 period. Malaysia is moving towards becoming one of the aged countries by 2030. The fast pace of ageing population is as a result of longer life expectancy and rapid decline in Total Fertility Rate (TFR).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ageing phenomenon: Malaysia towards 2030
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2017
Abstract: Statistics shows that those aged 60 years and above in Malaysia stood at 7.9 % in 2010 and the rate will reach 15.3 % by 2030, classified as one of the fastest nation to achieve aged country status within 20 years. This fast pace of ageing population is as a result of longer life expectancy and rapid decline in total fertility rate.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ageing in Asia: the way forward
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2012
Abstract: Ageing population is a universal phenomenon experienced by nearly all countries in the world at different rates. Malaysia, for example with a total population of 28.6 million in 2011, has experienced a steady rise in its older persons (those aged 60 years and above) from 6.3 % in 2000 to 7.7 % (or 2.2 million) in 2011. By 2020, it is estimated that the number of older persons in Malaysia will be 5.5 million and by 2030, older persons will constitute 15 % of the total population.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Elderly population
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2009
Abstract: The total population of the elderly (aged 60 and above) in Malaysia has reached to 2 million, that is 7 per cent out of the total of 27.6 million population. The proportion of the elderly is expected to exceed 10 per cent around the year 2025. Finding from the MPFS-4 focussed on living arrangements, elderly care, loneliness, community involvement, economic activities, sources of financial support and health status of the elderly. Data for this study was drawn from responses of a total of 1,866 elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population ageing
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2008
Abstract: According to United Nation’s estimates, 21 percent of the population in the developed countries was aged 60 years or over in 2005. This proportion is projected to increase to 28 percent in 2025 and 32 per cent in 2050. In countries where economies are in transition, the average proportion of the population aged 60 years or over was estimated at only 8 percent in 2005 but is expected to reach 13 percent by 2025 and nearly 20 percent by 2050. Thus, the number of older persons in the developing countries will likely more than double between 2005 and 2025. This increase is much larger than in the developed countries compared to countries where the economies are in transition, where the number of older persons will grow by about 44 percent and 32 percent respectively during the same period.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population growth and population ageing
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2005
Abstract: Population ageing has significant implications on the communities, families and the individuals, in the context of social change. With increasing age at marriage, more and more people are delaying family formation such that many retirees still have to support their young children. This means that there will be fewer resources for the older persons becomes increasingly serious as their earnings diminish after retirement. As life expectancy increases, the families may have to cope with more that one generation of older persons.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aging population in Malaysia: future challenges
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2001
Abstract: In the light of the growth of the older population, there is a need to respond to the increasing proportion and the absolute number of older persons in the total population. In Malaysia, unlike Japan and other developed countries, the issue of aging is not as critical. However, with increasing proportion and number of older persons, Malaysia has to plan early for the need of the older persons which are quite different from the rest of population.
|
|
|
|
Research Report (1)
|
|
Study on childcare & parenting styles among working parents in Peninsular Malaysia 1998
Item Type: Research Report
Editor:
Year: 00/00/1998
Abstract: The Study on Childcare and Parenting Styles among working Parents in Malaysia is one of the three research issues on the family that has been identified by the Ministry of National Unity and Social Development under the "Pelan Induk Tindakan Sosial (PINTAS)". This survey is timely in view of the many challenges faced by Malaysian families who have been affected directly or indirectly by modernisation, urbanisation and industrialisation as a result of socio-economic development. Female labour force participation has increased from 37 per cent in 1970 to 42 per cent in 1991 and is expected to reach 52 per cent by year 2000. The objectives of the study were: • To study the current situation in childcare arrangements among working parents and to elicit suggestions from them regarding improvements in childcare. • To study parenting styles among working parents and to make recommendations for better parenting practices. • To use findings from the study as an input towards designing strategies and programs for the betterment of families. • To obtain indicators on childcare and parenting for the monitoring of goals and targets in the National Plan of Action on Children.
|
|
|
|
Scientific Poster (1)
|
|
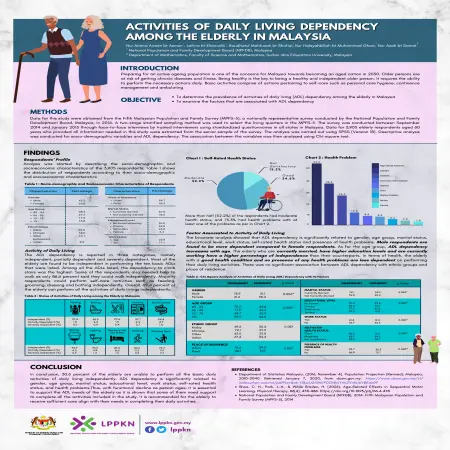
Activities of daily living dependency among the elderly in Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The objective of this study is to determine the prevalence of activities of daily living (ADL) dependency among the elderly in Malaysia and to examine the factors that are associated with ADL dependency.
|
|
|
|