Browse by Subject
Results for Search : "305 Social groups"
|
|
Fatherhood program and children’s development: Does it mature?
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The prevalence of social problems and criminal cases among teenagers in Malaysia is at an alarming level. Often, such problems are associated with the fragility of the family institution underpinned by the role of the father. In Malaysia, fatherhood-related programs are still limited and minimal compared to the United States where most initiatives to support fathers have been implemented through father-specific programs designed to improve fathers' economic self-sufficiency, parenting knowledge and skills.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertility preferences in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 30/11/2018
Abstract: Most countries have been experiencing changes in fertility pattern over the last few decades. Fertility transition from high to low is a relatively recent phenomenon in Malaysia. The total fertility rate (TFR) had declined from 4.9 children per woman in 1970 to 4.0 in 1980. It has continued to fall and has reached the replacement level of 2.1 in 2010. This chapter provides the trend analysis and a comparative analysis of fertility trends to explain the fertility transition of Malaysia’s population. Data used in this study were obtained from Department of Statistics, Malaysia and Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2014. The result of this study showed that the fertility rate between age groups was higher among Malay than other ethnics since 1991–2010. Across all ages, the fertility rate has a negative correlation with the educational level where women with tertiary education tend to have fewer children compared to less educated women. This study also presents the fertility desire in Malaysia. There is a negative correlation between age group and fertility desire. In addition, the desire to stop childbearing is found to be stronger when women have had three living children. The findings of this study will help policy makers to plan programmes to improve the fertility rate in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
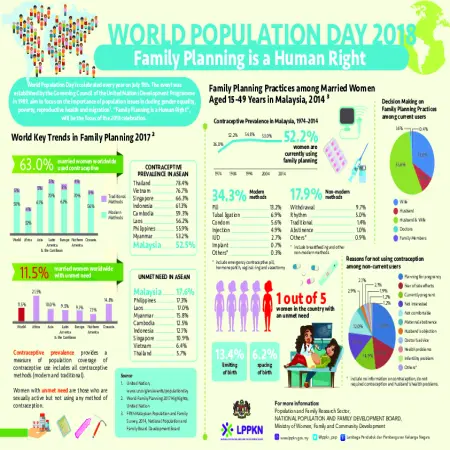
Family planning is a human right
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2018
Abstract: World Population Day is celebrated every year on July 11th. The event was established by the Governing Council of the United Nations Development Programme in 1989, aim to focus on the importance of population issues including gender equality, poverty, reproductive health and migration. Family Planning is a Human Right, will be the focus of the 2018 celebration.
|
|
|
|
|
|
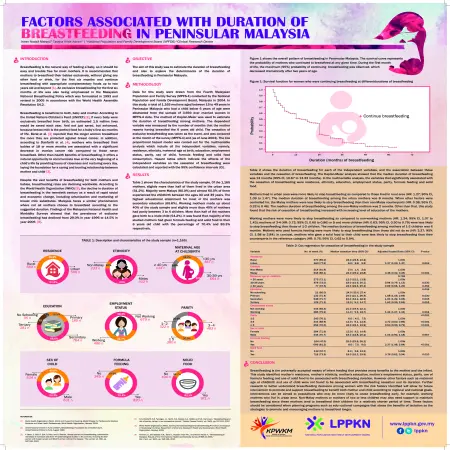
Factors associated with duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breastfeeding is the natural way of feeding a baby, so it should be easy and trouble free for most mothers. It is recommended that mothers to breastfeed their babies exclusively, without giving any other food or drink, for the first six months and continue breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods up to two years old and beyond [1]. An exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life was also being emphasized in the Malaysian National Breastfeeding Policy which was formulated in 1993 and revised in 2005 in accordance with the World Health Assembly Resolution 54.2. Breastfeeding is beneficial to both, baby and mother. According to the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) [2], if every baby were exclusively breastfed from birth, an estimated 1.5 million lives would be saved each year. And not just saved, but enhanced, because breast milk is the perfect food for a baby’s first six months of life. Beral et al. [3] reported that the longer women breastfeed the more they are protected against breast cancer. In addition, according to Danforth et al. [4], mothers who breastfeed their babies of 18 or more months are associated with a significant decrease in ovarian cancer risk compared to those never breastfeed. Other than health benefits of breastfeeding, it offers a natural opportunity to communicate love at the very beginning of a child’s life by providing hours of closeness and nurturing every day, laying the foundation for a caring and trusting relationship between mother and child [2]. Despite the vast benefits of breastfeeding for both mothers and babies, breastfeeding rates are declining worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [5], the decline in duration of breastfeeding in the twentieth century as a result of rapid social and economic change, including urbanization and marketing of breast milk substitutes. Malaysia faces a similar phenomenon where not all mothers choose to breastfeed according to the suggested duration. Findings of the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Surveys showed that the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding had declined from 29.0 % in year 1996 to 14.5 % in year 2006 [6]. Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the duration of breastfeeding and also to explore the determinants of the duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign workers in Malaysia: assessment of their economic effects and review of the policy
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study aims to help Ministry of Human Resource to better manage existing human resources in the country and to plan for the development of future human capital needs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertility and religion in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This paper presents a summary of literature review on the subject of religious fertility differential for a research at the Institute of Graduate Studies, University of Malaya and initial results from investigations using the MPFS 41 (Peninsular Malaysia) data. Conceptual frameworks due to Davis and Blake (1956) and Bongaarts (1978) are used to construct a framework of data analysis using SPSS, concentrating on one-way ANOVA and Stepwise Multiple Regression. Next, the influence of religion on age-at-firt-marriage is compared to that of education level, pre-marital working experience and place of residence. Similar to studies done elsewhere, Muslims in Peninsular Malaysia have the highest fertility level and the lowest age at first marriage.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financial beliefs and behaviour of college students: cultural differences
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2004
Abstract: This study compared the financial beliefs and behaviour of college students in two different cultures; Malaysia and United States. Using the social learning framework, the study assumed that children socialized in different culture will have different beliefs and behaviours. Two sets of data used were data from 665 college students Iowa State University (ISU)and convenience sampling of data from self administered questionnaires among 366 students of University Putra Malaysia (UPM). The result of the study revealed some similarity but many more differences. Cultural practices, economic and social environment influenced financial beliefs and behaviour of college students in both cultures. Service available and rules and regulations influence accessibility to services and choices available. ISU students was displaying favourable financial behaviour compared to UPM students. Students need to be aware and understand financial complexity to help them manage limited financial resources while studying as well as prepare them for work life.
|
|
|
|