Browse by Subject
Results for Search : "303 Social processes"
|
|
Peranan, tahap kesejahteraan, cabaran dan persediaan golongan wanita dalam menghadapi situasi pandemik covid-19 di Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2023
Abstract: Towards post COVID-19, most of the daily routines of Malaysian women's life have changed. The change in routine includes the management of household affairs, work routine to work from home (work from home) and socializing routine. As a result, society, especially women, is seen as increasingly depressed due to the loss of sources of income, limited involvement in outdoor activities and problems in balancing work and family time. Aware of this situation, the National Population and Family Development Board Malaysia (NPFDB) has taken the initiative to conduct a series of public opinion surveys throughout 2020 and 2021. This study aims to explore the role, level of well-being, challenges and preparations of women in facing the pandemic situation COVID-19 in Malaysia. This study is an online survey study. The findings of this study are a reflection of the current situation of society and family institutions in Malaysia in facing several new waves during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings of the survey show that women are more affected than men, but the level of well-being of women in Malaysia is seen to be still at a satisfactory level. In addition, the results of the study also found that women stated that they are faced with various issues and challenges especially for those who are married. Issues of family management, children's education at home and more flexible working hours should be highlighted for consideration by the Government. It is hoped that various initiatives and development plans related to women can be planned in addition to strengthening existing policies towards achieving the aspiration of "Building a CIVIL Malaysia". In general, the chapters in this book contribute to knowledge related to the current situation of women in facing the new normal life. While in particular, the chapters in this book contribute to knowledge related to the role, well-being, challenges and preparation of Malaysian women in facing the situation of the COVID-19 pandemic.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jangan Malu Ambil Tahu, Jangan Malu Bagi Tahu
Item Type: Video
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2023
Abstract: #AmbilTahuBagiTahu is a movement that supports the campaign "Don't be ashamed to learn and don't be ashamed to learn" which aims to raise awareness about the importance of reproductive and social health education in Malaysia.
This campaign is implemented by one of the agencies under the Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development which is the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population and sustainable development, in particular sustained and inclusive economic growth
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2022
Abstract: In 2020, Malaysia's population was at 32.4 million, growing at an average annual rate of 1.7 per cent for the period from 2010 to 2020. Driven by a decline in fertility rate accompanied by a sustained rise in life expectancy. Malaysia will become an aged nation by 2030.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 55th session of the Commission on Population and Development United Nations, New York, 25-29 April 2022
Item Type: Country Statement
Editor:
Year: 00/04/2022
Abstract: Malaysia’s socio-economic development has been significant in transforming our economy from a low income to an upper-middle-income status. We have achieved significant progress in eradicating poverty and narrowing inequalities. However, the COVID-19 crisis has resulted in vulnerable households falling into poverty and hardship.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population, food security, nutrition and sustainable development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: Malaysia occupies a commendable position in the 2019 Global Food Security Index, jumping to 28th place as compared to 48th in 2018. The national level food availability data indicates that there are sufficient supply of major food commodities for the population. All major foods are available in sufficient quantities to meet the market demands. Food access is no longer an issue for most Malaysians, with better processing, transport and storage systems and distribution arrangements.
|
|
|
|
|
|
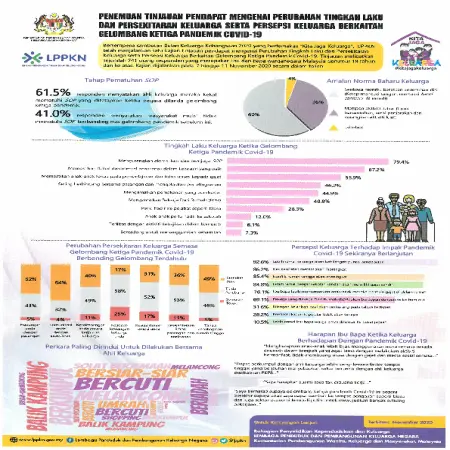
Penemuan tinjauan pendapat mengenai perubahan tingkah laku dan persekitaran keluarga serta persepsi keluarga berkaitan gelombang ketiga pandemik Covid-19
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2020
Abstract: This infographic is about findings from public opinion poll that was conducted in conjunction with the 2020 National Family Month celebration themed "Kita Jaga Keluarga". The survey involved a total of 741 respondents who are parents of Malaysian citizens aged 18 years and above.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 52nd session of the commission on population and development:general debate on review and appraisal of the programme of action of the international conference on population and development and its contribution to the follow-up and review of the 2030 agenda for sustainable development
Item Type: Country Statement
Editor:
Year: 01/04/2019
Abstract: The population of Malaysia has increased more than three-fold from 10.5 million in 1970 to about 33 million today. the population was growing around 2.5 percent per annum for the period 1970-2000 but it has declined to 1.7 percent between 2010 and 2018.
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 Years of the ICPD: reproductive health and rights challenges
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2019
Abstract: To increase contraceptive prevalence will require strengthening the information, education and skills development of health care providers, repositioning of family planning, more public awareness on benefits and side effects of modern contraceptives, keeping abreast with modern contraceptive technology including LARC, male/boy responsibility programs, better data collection and monitoring including from the young and unmarried, collaboration and coordination with all stakeholders and delivery of quality services to all without discrimination and stigmatization.
|
|
|
|