Browse by Author
|
|
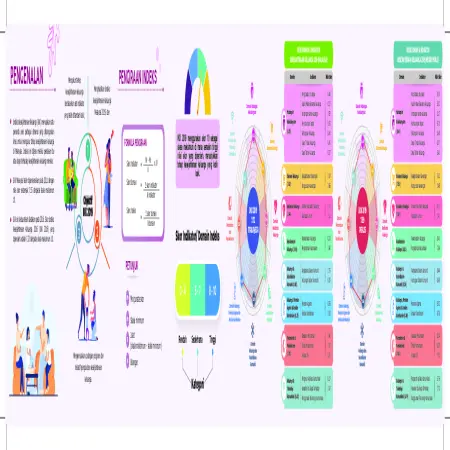
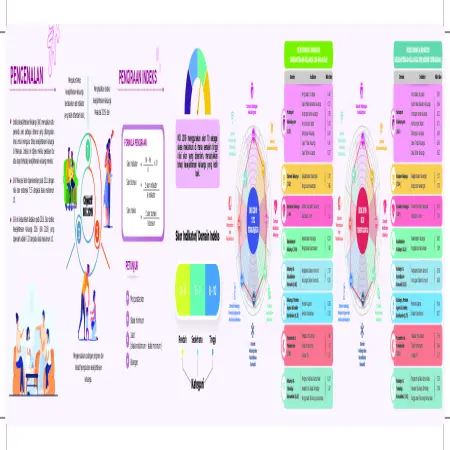
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Negeri Perak
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi-dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. .The Family Well-Being Index Score for Perak was 7.17 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
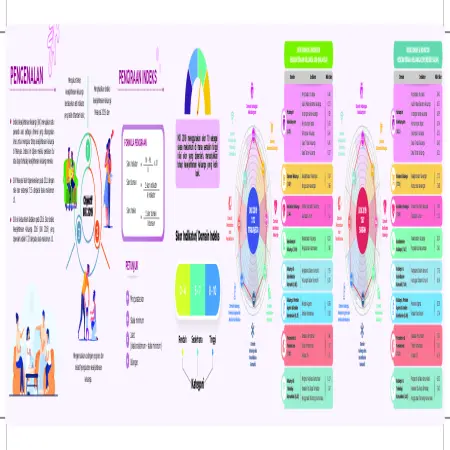
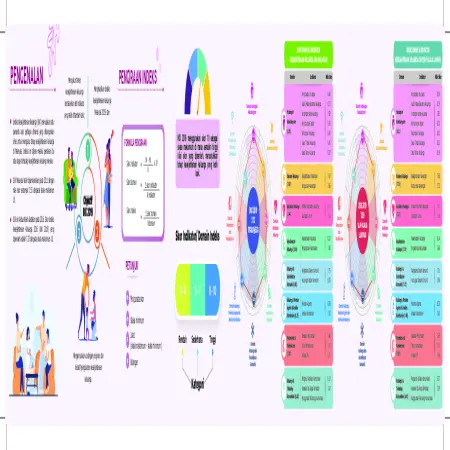
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Negeri Perlis
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi-dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for Perlis was 7.99 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
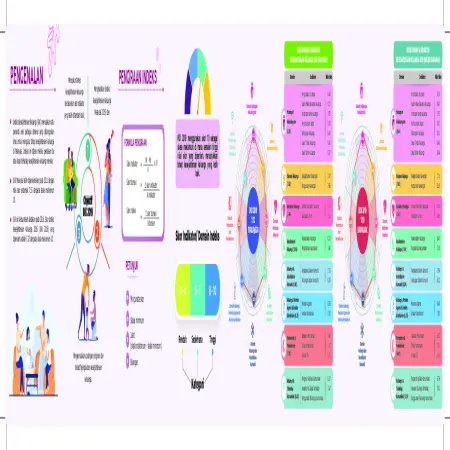
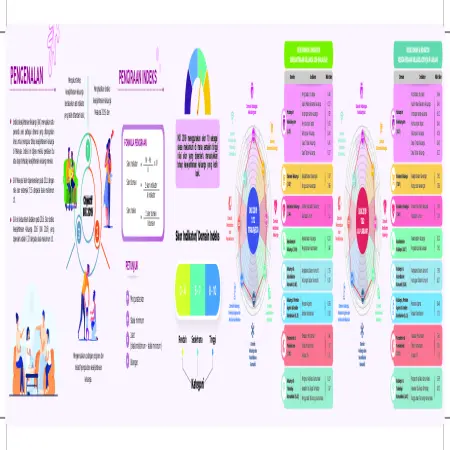
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Negeri Sabah
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi-dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for Sabah was 7.67 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
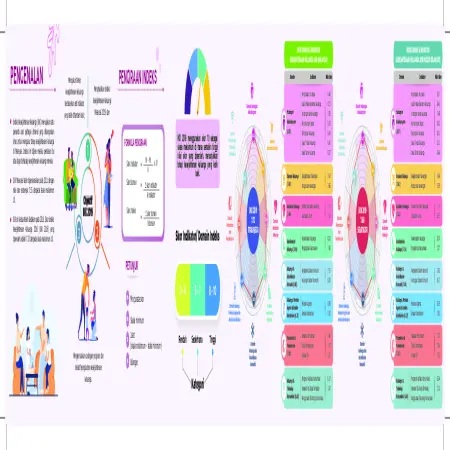
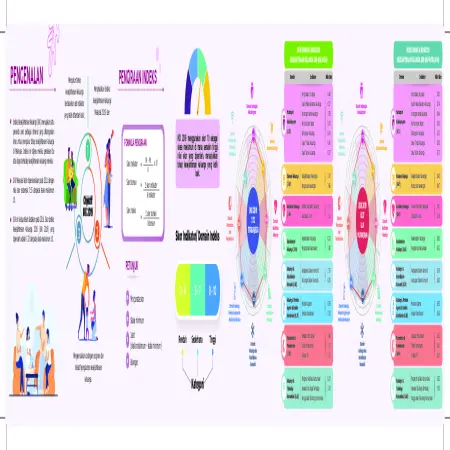
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Negeri Sarawak
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi-dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for Sarawak was 7.78 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019(IKK 2019) Negeri Selangor
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi -dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for Selangor was 7.68 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Negeri Terengganu
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi -dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for Terengganu was 8.10 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the high level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indeks Kesejahteraan Keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Wilayah Persekutuan Kuala Lumpur
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi -dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur was 7.59 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indeks Kesejahteraan keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Wilayah Persekutuan Labuan
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi -dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for the Federal Territory of Labuan was 7.82 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indeks Kesejahteraan keluarga Malaysia 2019 (IKK 2019) Wilayah Persekutuan Putrajaya
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The Family Well -Being Index (FWBI) is a multi-dimensional benchmark specially developed to measure the level of family well -being in Malaysia. This index is generated through a mother’s or father’s assessment of their family’s well-being. The Family Well-Being Index Score for the Federal Territory of Putrajaya was 8.37 from a maximum score of 10, which was at the high level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insights into the well-being of dual earner families in Malaysia: findings from the Malaysian Family Well-Being Index Study 2019
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: Traditionally, GDP has been used as a measure of a country’s level of development, and the quality of life of citizens. Of late, the happiness index has gained increasing attention, as a measure of well-being, to include income distribution and non-financial aspects, such religious and spiritual well-being, and inter-personal relationship. Malaysia has conducted three rounds of the family well-being surveys to provide inputs for the five-year development plans. The overall family well-being score among dual earner families in Malaysia was 7.84 out of a maximum scale of 10, which is at the moderate level.
|
|
|
|