Browse by Author
Results for Family Name : "Mahmud" AND Given Name/Initial : "Adzmel"
Article (6)
|
|
Comparison of rural and urban contraceptive methods preferences among married women in Malaysia, 2018
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 30/05/2021
Abstract: Contraceptive use among women remains an important public health intervention. Imperatively, the equality of family planning access between rural and urban areas allows all women to have the same opportunities to receive family planning service towards better well-being of families.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subjective well-being of the Malaysian citizen: preliminary development of survey instrument
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/03/2020
Abstract: A questionnaire is a well-known measurement instrument used by most of the researchers when conducting a survey. It is a powerful tool for collecting data in survey research. It should be noted that the quality of a measurement instrument used plays a key role in ensuring the quality of data gained in the survey. Therefore, it has become essential for the researchers to carefully design their questionnaire so that the quality of the data obtained can be preserved. Then, it is also vital for the researchers to assess the quality of the data obtained before it can be successfully used for further analysis. This article discussed an early process involved in development of the survey instrument for the purpose of assessing subjective well-being of the Malaysian citizen. These include operationalization of definition, identification of the important dimension and indicators of subjective well-being, rating scale and content validity of the items with the experts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Household income and life satisfaction of single mothers in Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2020
Abstract: Single parenting is not an uncommon family setting in Malaysia. Past studies, however, tend to confirm that increasing number of single mothers is also related to increasing number of households living in poverty. Issues on single mothers in Malaysia has initiated many social groups, non-governmental organizations and government agencies to step in eradicating poverty among the single mothers especially those fall in the B40 income groups. Until today, the current information available on single mothers in Malaysia is still limited. This study attempts to explore the socio – demographic and economic background of single mothers in Malaysia and to examine their income category and level of poverty. This study utilizes the Fifth Malaysian Population Survey (MPFS5) data. MPFS5 is a nationally representative large-scale research conducted by the National Population and Family Development (NPFDB) in 2014. However, for this study, the target respondents are working single mothers (either widowed, divorced, separated); aged 15 – 59 years old; residing in Peninsular Malaysia and have children staying together with them. Findings from this study reveal that household income of single mothers falls under the B40 category but there is not enough evidence to claim that their household income is below the poverty line. Chi – Square test of associations prove relationships between poverty level to socio – demographic variables such as level of education and residential states, while PLS – SEM techniques show that income category of single mothers is somehow related to the predictors of life satisfaction construct and the overall life satisfaction. Suggestions for some policy recommendations to protect and promote single mothers within the informal sectors is also presented.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Development of Malaysian women fertility index
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2018
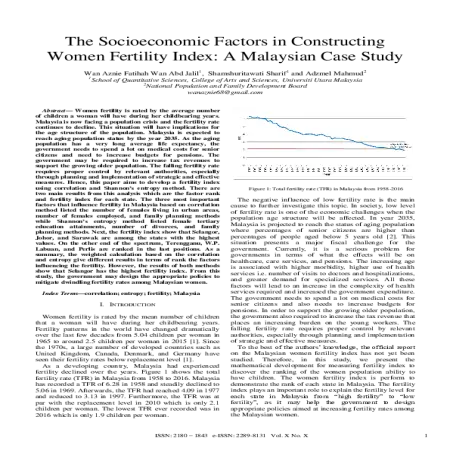
Abstract: A fertility rate is a measure of the average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years. Malaysia is now facing a population crisis and the fertility rate continues to decline. This situation will have implications for the age structure of the population where percentages of senior citizens are higher than percentages of people aged below 5 years old. Malaysia is expected to reach aging population status by the year 2035. As the aging population has a very long average life expectancy, the government needs to spend a lot on medical costs for senior citizens and need to increase budgets for pensions. The government may be required to increase tax revenues to support the growing older population. The falling fertility rate requires proper control by relevant authorities, especially through planning and implementation of strategic and effective measures. Hence, this paper aims to develop a fertility index using correlation and Shannon's entropy method. The results show that Selangor, Johor, and Sarawak are among the states with the highest values of the fertility index. On the other end of the spectrum, Terengganu, W.P. Labuan, and Perlis are ranked in the last positions according to the fertility index. The information generated from the results in this study can be used as a primary source for the government to design appropriate policies to mitigate dwindling fertility rates among Malaysian women.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The socioeconomic factors in constructing women fertility index: a Malaysian case study
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 01/06/2017
Abstract: Women fertility is rated by the average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years. Malaysia is now facing a population crisis and the fertility rate continues to decline. This situation will have implications for the age structure of the population. Malaysia is expected to reach aging population status by the year 2035. As the aging population has a very long average life expectancy, the government needs to spend a lot on medical costs for senior citizens and need to increase budgets for pensions. The government may be required to increase tax revenues to support the growing older population. The falling fertility rate requires proper control by relevant authorities, especially through planning and implementation of strategic and effective measures. Hence, this paper aims to develop a fertility index using correlation and Shannon's entropy method. There are two main results from this analysis which are the factor rank and fertility index for each state. The three most important factors that influence fertility in Malaysia based on correlation method listed the number of females living in urban areas, number of females employed, and family planning methods while Shannon's entropy method listed female tertiary education attainments, number of divorces, and family planning methods. Next, the fertility index show that Selangor, Johor, and Sarawak are among the states with the highest values. On the other end of the spectrum, Terengganu, W.P. Labuan, and Perlis are ranked in the last positions. As a summary, the weighted calculation based on the correlation and entropy give different results in terms of rank the factors influencing the fertility. However, the results of both methods show that Selangor has the highest fertility index. From this study, the government may design the appropriate policies to mitigate dwindling fertility rates among Malaysian women.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socio-economic determinants of pap smear screening among married women in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/02/2013
Abstract: This study is to identify the influences of socio-economic factors towards the practice of Pap smear screening among ever married women. Bivariate correlations and logistic regression analysis was applied to the data set containing 3,283 ever married women age 15-49 years, interviewed during the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2004. It was found that only half the women had undergone Pap smear screening prior three years of survey, in which Chinese had the highest percentage of Pap smear screening. The logistic statistical analysis also had identified several variables has important determinant has of Pap smear screening for ever married women. Finding from this study suggest a significant relationship between the cervical cancer awareness and knowledge, age and ethnicity for those women who practice Pap smear screening.
|
|
|
|
Book Section (4)
|
|
Perceived social support, mental health and quality of life among recipients of old age financial assistence
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: The present study examines multidimensional perceived social support, mental health and quality of life (QOL) in older adults aged 60 years and older who receive the financial assistance provided by the Department of Social Welfare. A cross-sectional study approach was conducted among 487 older adults living in Selangor, Malaysia, who are the recipients of old age financial assistance known as Bantuan Warga Emas (BWE).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kemiskinan haid: analisis pengetahuan, sikap dan amalan pengurusan menstruasi di Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is very important in the social and economic development of a country, especially Malaysia. It refers to physical and emotional well-being, also including the ability to be free from unplanned pregnancy, unsafe abortion, domestic violence, sexually transmitted diseases, AIDS/HIV and good and perfect menstrual management. The issues of period poverty has gained attention in Malaysia although it is not a new social phenomenon. The issue of poverty exacerbated by the Covid-19 pandemic has become a cancer in the discussion of period poverty.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fertility preferences in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 30/11/2018
Abstract: Most countries have been experiencing changes in fertility pattern over the last few decades. Fertility transition from high to low is a relatively recent phenomenon in Malaysia. The total fertility rate (TFR) had declined from 4.9 children per woman in 1970 to 4.0 in 1980. It has continued to fall and has reached the replacement level of 2.1 in 2010. This chapter provides the trend analysis and a comparative analysis of fertility trends to explain the fertility transition of Malaysia’s population. Data used in this study were obtained from Department of Statistics, Malaysia and Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2014. The result of this study showed that the fertility rate between age groups was higher among Malay than other ethnics since 1991–2010. Across all ages, the fertility rate has a negative correlation with the educational level where women with tertiary education tend to have fewer children compared to less educated women. This study also presents the fertility desire in Malaysia. There is a negative correlation between age group and fertility desire. In addition, the desire to stop childbearing is found to be stronger when women have had three living children. The findings of this study will help policy makers to plan programmes to improve the fertility rate in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Malaysian Family Wellbeing Index
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2017
Abstract: Family institutions need to be strengthened to balance the rapid process of social and economic development of the country. This is important because the family is the basic social unit that prepares the supplies the human capital for the national development. Given the importance of family wellbeing for the future of the nation, scientific studies ought to be conducted to measure the wellbeing of families in this country.
|
|
|
|
Conference or Workshop Item (11)
|
|
The association between work family conflict and social demographic characteristics among fathers in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: Those living in urban, Indian, age 30-44 years, higher educational level, single father, and non Muslim’s tend to face Work Family Conflict than their counterparts. More hectic/busy environment and higher cost of living in urban area compared to the rural area may contribute to the Work Family Conflict among fathers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Household income and life satisfaction of single mothers in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/03/2020
Abstract: This study attempts to explore the socio –demographic and economic background of single mothers in Malaysia and to examine their income category and level of poverty. This study utilizes the Fifth Malaysian Population Survey (MPFS5) data. However, for this study, the target respondents are working single mothers (either widowed, divorced, separated); aged 15- 59 years old; residing in Peninsular Malaysia and have children staying together with them. Findings from this study reveal that household income of single mothers falls under the B40 category but there is not enough evidence to claim that their household income is below the poverty line. Chi – Square test of associations prove relationships between poverty level to socio – demographic variables such as level of education and residential states, while PLS – SEM techniques show that income category of single mothers is somehow related to the predictors of life satisfaction construct and the overall life satisfaction. Single mothers are already facing limited job market and reduced salary with their low level of educational attainment. Therefore, some suggested policy recommendations are to protect and promote single mothers involved in elementary occupations and to create more quality jobs to develop these women from the existing low-paid of the informal into the formal sectors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mendepani cabaran sasaran SDG 2030: memenuhi keperluan kontraseptif di Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2019
Abstract: This paper will present on the trends and achievements of contraceptive use rates, unmet contraceptive requirements and modern contraceptive demands met. In addition, the presentation will also touch on issues and challenges on the rate of contraceptive use which is still hovering around 50 to 52 percent over the past three decades as well as the level of unmet needs in Malaysia which is relatively high compared to other Asean countries.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pengenalan Kajian Penduduk dan Keluarga Malaysia Kelima 2014
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2016
Abstract: The objective of this study to provide time series data related to demographic and socioeconomic information and to be source of data for national socioeconomic planning. Tha last objective is to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of planning and implementation of policies, programs and activities. This slide presentation is about the introduction and key findings of the Malaysian Population and Family Survey-5, 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Determinants of loneliness among elderly in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2016
Abstract: As of 2014, there is an estimated of 2.7 million elderly in Malaysia or 8.9% out of the total population of 30.3 million. Recent projections estimated that Malaysia will become an ageing nation by 2035 when 15% of the population falls into this group. As the number of the elderly population continues to grow, loneliness is becoming one of the major issues leading to impaired quality of life among elderly. Loneliness might lead to mental problems and stress among the elderly. This study attempts to examine the characteristics and influencing factors of loneliness among elderly in Malaysia. Data for this study is a sub-sample of a bigger national study gathered through the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5) conducted in 2014 by the National Population and Family Development Board Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi penglibatan wanita berkahwin dalam tenaga buruh di Semenanjung Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: This study is to identify the influences of socio-economic factors towards the labour force participation among married women in Peninsular Malaysia. Bivariate correlations and logistic regression analysis was applied to the data set containing 2,366 married women aged 15-49 years, interviewed during the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2004. It was found that only half of the women were currently working. Chinese had the highest percentage who were currently working as compared to the Malays and Indians. The logistic statistical analysis had also identified several variables which were important determinants of the current work status of married women. Based on logistic statistical analysis, it was found that stratum, previous occupation prior to marriage and presence of young children had significant relationships to women’s participation in the labour force.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kesan amalan dan status kesihatan terhadap kemurungan di kalangan warga tua lelaki di Semenanjung Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This study aims to look at the factors of practice and health status that contribute to depression among elderly men aged 60 years and above in Peninsular Malaysia. The data used in this study was obtained from the 4th Malaysian Population and Family Survey which was conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (LPPKN). The data obtained were analyzed using Descriptive Statistics and Logistic Regression. Among the variables used were the level of health, frequency of treatment, disease, frequency of exercise and health check-ups. The results of the analysis showed that coronary heart disease, decreased labor capacity, restless inability to sleep and attending religious ceremonies were independent variables influencing the risk of depression.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Keinginan kesuburan
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: The decline in fertility rates in Malaysia is happening rapidly and it is expected that the rate will reach the replacement level (replacement level = 2.1) in 2015. A woman's desire/decision to have a child has a direct impact on the fertility rate and population growth. Thus, the study aims to identify the factors that influence women's desire to have children or do not need to be implemented. Data and Methodology: This paper presents the preliminary findings of the study Fertility at the Crossroad: Children Now, Later or Never conducted by LPPKN in 2012. This study uses a cross -sectional survey design method with a focus on women in the reproductive age group. 15-49 years working in the public sector in Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya and Selangor. The method of data collection was through face -to -face interviews and self -administered using a questionnaire. Through stratified sampling method, a total of 98 public sector agencies were selected. To achieve the objectives of the study, the data obtained were analyzed using Descriptive Statistics, Chi Square and Logistic Regression (Forward LR Method). The dependent variable studied was the desire to have children (0 = do not want more children, 1 = want more children). While there are nine (9) independent variables studied namely age, ethnicity, education level, job grade (Management and Professional/Support), income, number of childbirths, pregnancy history (miscarriage/stillbirth/abortion), fertility problems and The husband lives far away. Findings: In total, a total of 1,898 data for women working in the public sector were analyzed. A total of 75.9% of respondents have a desire to have children. The results of Chi -Square analysis showed that the variables of age, ethnicity, income, number of births, pregnancy history, fertility problems and husbands living far apart had a significant relationship with the desire to have children. However, there is no evidence to suggest that post grade has a relationship with childbearing desire. Logistic regression test (Forward LR Method) showed that 57.8% of the variation in women's desire to have children can be explained by four independent variables, namely fertility problems, ethnicity, age and number of births. Conclusion: The results of the study found that women's desire to have children can be considered high. To support women's desire to have children, various forms of assistance/support should be provided by the employer/government. Among the main assistance/support needed are childcare centers at work, holiday facilities to care for sick children, subsidized childcare costs and full-paid facilities for children in need of special care.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kajian pekerja Indonesia di Bahagian Tawau, Sabah: pengenalan kajian
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2011
Abstract: The objective of this study is to identify the causal factors of entry and conduct socio-demographic analysis such as family, education, health, family planning practices, citizenship and socialization of Indonesian immigrants. The next objective is to study the perception of dependence on Indonesian workers as well as the impact of the presence of immigrants/Indonesian workers on the local population in terms of economy, security, family, culture, education, health, social and legal. The last objective is to identify the factors of hiring foreign workers, the process and costs of hiring, wages and employment, and the facilities provided by employers to foreign workers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socio-economic correlates of fertility in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2010
Abstract: To examine fertility trends and differentials among women in Peninsular Malaysia by selected socioeconomic variables which significantly influence the number of children ever born. A total of 3,697 ever-married women aged 15-49 were successfully interviewed in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
Scientific Poster (2)
|
|
Why do men and women remain single? Findings from the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5)
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 01/07/2015
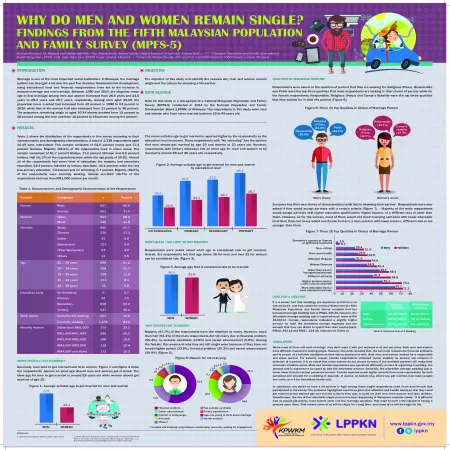
Abstract: Marriage is one of the most important social institutions. In Malaysia, the marriage pattern has changed a lot over the past few decades. Socioeconomic development, rising educational level and financial independence have led to the increase in delayed marriage and non-marriage. Between 1980 and 2010, the singulate mean age at first marriage among men and women increased from 26.6 years and 23.5 years to 28.0 years and 25.7 years, respectively. Among men aged 25-29, the proportion never married had increased from 40 percent in 1980 to 53 percent in 2010, while that of the women had also increased from 21 percent to 38 percent. The proportion remaining single at aged 30-34 almost doubled from 15 percent to 28 percent among the men and from 10 percent to 18 percent among the women. The objective of this study is to identify the reasons why men and women remain single and the criteria for choosing a life partner.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intention to limit childbearing among working women
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2013
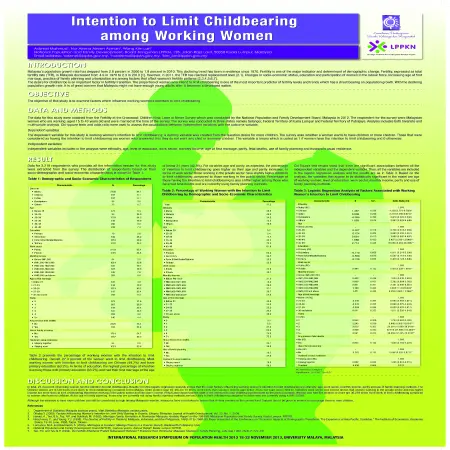
Abstract: Malaysia's population growth the rate has dropped from 2.6 percent in 2000 to 1.9 percent in 2010. This declining trends has been in evidence since 1970. Fertility is one of the major indicator and determinant of demographic change. Fertility, expressed as total fertility rate (TFR), in Malaysia decreased from 4.9 in 1970 to 2.3 in 2010. However, in 2011, the TFR has reached replacement level (2.1). Changes in socio-economic status, education and participation of women in the labour force, increasing age at first marriage, practice of family planning and urbanization are among factors that affect women's fertility pattern.
|
|
|
|
Thesis (1)
|
|
Socio-economic correlates of fertility in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 01/04/2009
Abstract: The main aim of this paper is to examine the fertility trends and differentials among Peninsular Malaysia women based on the 2004 Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-4) according to selected socio-economic variables which were found to have significant effect on number of children ever born. Findings from the study reveal that mean number of children ever born has dropped from 4.2 children in 1974 to 3.6 children in 1984, 3.4 children in 1994 and continued to decline to 3.1 in 2004. Fertility level is highest among Malays, who resides in rural areas, eastern region, lower educational level, women who had never worked, women whose husbands worked in agricultural sector and family income less than RM1000 a month. Socio-economic variables can only affect the fertility level through the intermediate variables such as postponement of marriage and use of contraception. There is an upward trend in age at first marriage from 17.6 years in 1974 to 22.0 years in 2004. Marriage postponement is more pronounced among highly educated Chinese women, followed by the Indians and the Malays. The contraceptive prevalence rate was highest among Chinese, followed by the Indians and the Malays. Ethnic differentials in number of children ever born are rather pronounced. In the multivariate context, after adjusting for age and age at first marriage, the differential in the mean number of children ever born among ethnic groups remain discernible. The socio¬economic variables have different effects on the fertility level of each ethnic group. 'Region' emerges as the most important predictor of Malay fertility, while 'work pattern' and 'family income' is the most important predictor of Chinese and Indian fertility respectively. Based on the present trend, it is highly likely that the fertility will reach replacement level by 2020, and the 70 million population target is unlikely to be achieved through natural increase. There is a need for the government to give some attention to the trend in delayed and non-marriage as this will determine to a large extent the future course of population growth in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|