TOPICS
Results for Topics : "Education"
2023 (10)
|
|
Using games to stimulate and motivate Esl students in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Vocabulary is a vital part of English second language education. Unfortunately, the teaching and learning process is challenging for students as regular classroom activities have become tedious and boring, which does not motivate them to learn. Not only that, but this also discourages them from practising outside of the classroom. To help encourage students to become more motivated in learning and improving their English vocabulary, teachers need to consider more creative activities to be used in the classroom.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Usability of ‘Rancanglah’ for health education in family planning: the perspective from healthcare personnel
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Advancement of digital technology brings great potential to complement current method in promoting family planning. Traditionally, health education on family planning is routinely delivered through face-to-face counseling during postnatal follow up at 6 weeks post-delivery. The innovation of RancangLah, a mobile-based application aims to educate women to choose the best family planning method for them apart from having awareness on their pregnancy risk.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Melaporkan kualiti tinjauan sistematik amalan bersesuaian pendidikan untuk kanak-kanak bawah dua tahun: Pematuhan mengikut garis panduan Prisma
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: The aim of this study was to assess the quality of the reporting of the systematic review of educationally appropriate practices for children under two years of age using the guidelines of the Item Pelaporan Pilihan for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (PRISMA). Results of searches from Scopus, Web of Science (WoS), and Taylor & Francis online have obtained 42 journal articles of empirical report data that describe the education of children under two tears of age starting in 2019-2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kepentingan pendidikan keusahawanan bagi mengurangi jurang kemiskinan dalam mencapai matlamat pembangunan mampan negara: kerangka konseptual
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: The study was conducted on the importance of entrepreneurship education in reducing the poverty gap between urban and rural population. This study aims to study the effectiveness of entrepreneurship education in changing the living standards of a family. Sustainable development requires an education that is effective in lifting students out of poverty. Poverty is a global problem not only faced by the country of Malaysia but the whole world is facing the same problem.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population, education and sustainable developmet
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2023
Abstract: Education is a longstanding right enshrined in human rights and developmental instruments, including in the Plan of Action also recognises the key role of education in sustainable development, as well as the responsibilities of different stakeholders, particularly parents, in this regard.
Strengthening of human capital through education is a priority to Malaysia, with the Government providing free education to citizens up to secondary level. Malaysia is also undertaking efforts to ensure that the education system is robust, resilient and fit for the future.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Population Policy Brief: Youth Sexual Education and Reproductive Health
Item Type: Act & Policy
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2023
Abstract: Comprehensive sexuality education (CSE) is a proven and cost-effective intervention program meant to promote healthy sexual behaviours, prevent unintended pregnancies, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and gender-based violence, and promote gender equality and human rights. Therefore Malaysian have to work together to foster universally accepted sex education within society by implementing a suitable tailored curriculum based on professionally-verified CSE.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 56th Session of The Commission On Population And Development, United Nations New York, 10-14 April 2023
Item Type: Country Statement
Editor:
Year: 11/04/2023
Abstract: Education is a longstanding right enshrined in human rights and developmental instruments, including in the Plan of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD). The ICPD Plan of Action also recognizes the key role of education in sustainable development, as well as the responsibilities of different stakeholders, particularly parents, in this regard. Investments in education systems are of utmost importance for population growth, as it empowers people to lead better, healthier and sustainable lives. For Malaysia, the education system serves as a fundamental component in our quest to be a developed nation, and in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Strengthening of human capital through education is a priority to Malaysia, with the Government providing free education to citizens up to secondary level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modul My Therapeutic Family: Family Psychological First Aid
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2023
Abstract: INTRODUCTION:-
KASIH Keluarga Ceria Program is a comprehensive initiative aimed to bolster the family institution in Malaysia, which is a cornerstone of national well-being. This program comprises two modules, namely:
i. Psychoeducation Module
ii. Support Group "My Therapeutic Family" Module
These modules were based on the Family Psychological First Aid (F-PFA) model, jointly developed by NPFDB and Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (UPSI). The model integrated fundamental family dynamics, functional family systems, and Psychological First Aid principles recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The Support Group "My Therapeutic Family" Module complements the Psychoeducation Module by focusing on maintenance, particularly in the post-intervention phase, addressing crisis management within the family unit.
The objectives of this program are:
1. Enhance parents' awareness regarding mental health and adaptive skills;
2. Educate parents with knowledge of Family Psychological First Aid (F-PFA);
3. Empower parents with referral skills for psychological assistance;
4. Establish support groups platform for parents; and
5. Forge intelligent collaborative network between NGOs, agencies, and referral experts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modul Psiko-Pendidikan "Family Psychological First Aid"
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2023
Abstract: KASIH Keluarga Ceria Program is a comprehensive initiative aimed to bolster the family institution in Malaysia, which is a cornerstone of national well-being. This program comprises two modules, namely:
i. Psychoeducation Module
ii. Support Group "My Therapeutic Family" Module
These modules were based on the Family Psychological First Aid (F-PFA) model, jointly developed by LPPKN and Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (UPSI). The model integrates fundamental family dynamics, functional family systems, and Psychological First Aid principles recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The Psychoeducation Module serves to impart knowledge on F-PFA concepts and skills necessary during the preparation and intervention phases of managing crises within the family unit. The module encompasses mental health screening, psychosocial intervention, and referral skill. Families, armed with F-PFA knowledge and skills, gain the capacity to adeptly respond during family crisis.
The objectives of this program are:
1. Enhance parents' awareness regarding mental health and adaptive skills;
2. Educate parents with knowledge of Family Psychological First Aid (F-PFA);
3. Empower parents with referral skills for psychological assistance;
4. Establish support groups platform for parents; and
5. Forge intelligent collaborative network between NGOs, agencies, and referral experts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jangan Malu Ambil Tahu, Jangan Malu Bagi Tahu
Item Type: Video
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2023
Abstract: #AmbilTahuBagiTahu is a movement that supports the campaign "Don't be ashamed to learn and don't be ashamed to learn" which aims to raise awareness about the importance of reproductive and social health education in Malaysia.
This campaign is implemented by one of the agencies under the Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development which is the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB).
|
|
|
|
2022 (3)
|
|
Dasar dan Pelan Tindakan Pendidikan Kesihatan Reproduktif dan Sosial Kebangsaan (PEKERTI) 2022-2025
Item Type: Act & Policy
Editor:
Year: 08/09/2022
Abstract: This new PEKERTI policy is applicable to every individual regardless of age and gender and takes into account ethnic, religious and cultural diversity. Focus will be given to producing a healthy population in terms of reproductive and sexual health based on high moral values and practicing responsible behavior and mutual respect for each other.
This PEKERTI policy has been streamlined to achieve 5 objectives which are to (i) increase the awareness of Malaysians regarding the importance of reproductive and social health education, (ii) develop evidence-based reproductive and social health education programs, (iii) develop human expertise and modernity in aspects reproductive and social health education, (iv) carry out research in aspects of reproductive and social health education and (v) ensure programs and services under this policy are continuously monitored and evaluated.
In order to achieve these 5 objectives that have been set, 5 Cores have been identified as policy implementation machinery namely (i) Advocacy, Promotion and Prevention, (ii) Comprehensive Reproductive and Social Health Education Covering All Age Levels, (iii) Human Capital and other Resources for Reproductive and Social Health education, (iv) Research and Development and (v) Monitoring and Evaluation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modul Latihan Jurulatih SMARTSTART 2.0 "Pra Perkahwinan"
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2022
Abstract: Introduction:-
SMARTSTART 2.0 Pre-Marriage Training the Trainers Trainer Module is a new module that has been processed more neat and organized as a result of creative ideas through the compilation of contents and activities based on observations related to the latest issues that often being the cause of divorce. This module is a standard reference and guideline specially prepared for the use of trainers to facilitate the learning process, teaching and guide the preparation of programme materials. Through this module, it is hoped that it can provide positive benefits especially to individuals or couples who want to get married or who are planning to start a family in order to be more physically, mentally, emotionally, spiritually and financially prepared.
Objectives:
To provide knowledge and skills to the participants about preparations towards marriage.
Program Duration:
2 day program
Target Participants:
Individuals or couples who want/plan to get married.
Interactive Content:
Promising difference through learning and delivery methods. Full involvement of participants through skills training and group activities.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modul Pendidikan Kesihatan Reproduktif dan Sosial ACE (Accurate, Comprehensive, Effective)
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2022
Abstract: LPPKN published an intervention module called Module ACE – Accurate, Comprehensive and Effective on 2021 as a product from The Youth Intervention Study: Best Practices for Youth Intervention Programs that was carried out in 2016. This module is suitable to be used for adolescents age 10 to 24 years old.
The ACE module covers comprehensive reproductive health and sexuality education which includes legislation on sexual violence, gender equality and human trafficking. The module has been implemented on targeted groups consist of youths and peer educators, and proven to expand their knowledge on reproductive health. The activities from the module are delivered using pedagogy method that encourage on two-way interaction and responsiveness.
|
|
|
|
2021 (1)
|
|
Penemuan tinjauan pendapat tekanan dan cabaran keibubapaan dalam mendepani gelombang baharu pandemik Covid 19
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/03/2021
Abstract: This infographic is about of the findings of the Opinion Survey "Stresses and challenges of parenting in the face of the new wave of the Covid-19 pandemic".
|
|
|
|
2020 (3)
|
|
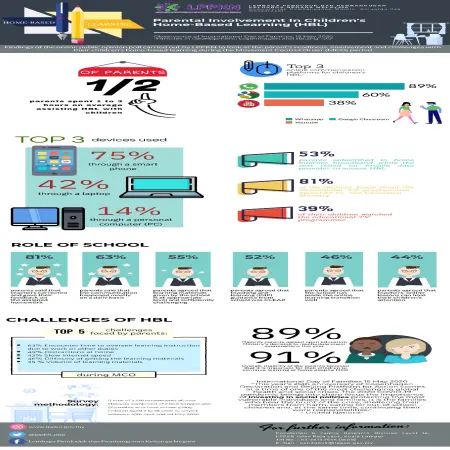
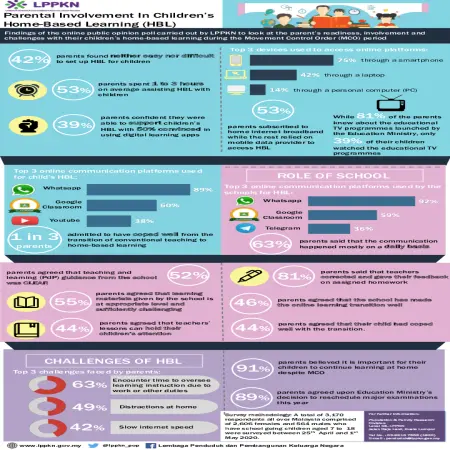
Parental involvement in children's home-based learning (HBL)
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2020
Abstract: This infographic is about findings of the online public poll carried out by National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) to look at the parent’s readiness, involvement and challenges with their children’s home-based learning during the movement control order (MCO) period.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The well-being of adolescents in divorced families
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2020
Abstract: This study aimed to explore an in-depth understanding on the wellness of teenagers in divorced families. This qualitative study used the phenomenological approach to explore the experience of ten teenagers living with single mothers after the divorce of their parents. Participants in this research are 10 teenagers age between 16 to 18 years’ old who lived with their mothers after their parents' divorce. The duration of their parents' divorce during the data collection was in the range of one to ten years. Data were collected using semi-structured interviews and document analysis by social media. Data were analysed using NVIVO12 software. Nine themes and 26 sub-themes emerged from this study. Three main themes and ten subthemes answered the first research question on, what is the meaning of wellness among teenagers in divorced families? Another three more theme and eight sub themes answered the second research question on, what are the perception of teenagers towards wellness in divorced families? The remaining three themes and eight sub themes answered the third research question on, how does divorce changes the wellness in teenager’s life? In conclusion, teenagers’ in this study accepted the changes that occurred as a result of parental divorce. The implications of this study is viewed from three aspects; 1) practical implications for professions such as counselors, 2) theoretical implications for future research, and 3) implications in the field of education for the wellness of the community. The information extracted from the findings of this study can help counselors to understand better on the actual living experience of teenagers in divorced families. The study also helps counsellors to understand how some teenagers manage to live a successful life and fulfilling all the wellness of life in spite of living in divorced families. As this study only focus on teenagers living with their mother after their parents’ divorce, it recommends future researchers to consider exploring areas of wellness among teenagers in joint custody parents or teenagers living with their single father after the parental divorce.
|
|
|
|
2019 (2)
|
|
Teen pregnancy and sex education
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2019
Abstract: Teenage pregnancy refers to any pregnancy in women or girls aged 19 years or younger. In 2016, the Ministry of Health recorded more than 12,000 teenage pregnancies in Malaysia. The National Registration Department reported that 4,992 children were born out of wedlock to girls aged 18 years and below. Teenage pregnancy is associated with immediate as well as long-term health risks. It is also accompanied by a number of negative consequences that are detrimental to the well-being of young mothers – disruption of education, limitation of opportunities for self-development and employment, social stigma and increased exposure to violence and exploitation. This article examines some circumstances resulting in teenage pregnancy and explores ways to support teenagers who face difficulties resulting from unintended pregnancy.
|
|
|
|
2018 (1)
|
|
Modul Cakna Diri Lelaki Pendidikan Kesihatan Reproduksi dan Seksual Untuk Remaja Lelaki Berumur 16-24 Tahun
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2018
Abstract: The Sexual and Reproductive Health Module for boys and young men age 16 to 24 years was developed to address sexual and reproductive health as well as social issues for boys and young men. It is also aim to create awareness on the importance of reproductive health and social education as well as gender equality for future well-being. This module is divided into two (2) main target groups i.e. general adolescents (Module A) and most-at-risk adolescents (Module B). The main components of Module A includes topics on adolescent growth, developmental, health, psychosocial - 3R (Respect, Relationship and Responsibility), laws and regulations, drugs and substance abuse. Module B covers topics on risky social behaviors, risky sexual behaviors and teen pregnancy. This module is developed as an interactive form using various learning methods such as role play, sketches, group work and discussions to attract participation of boys and young men.
|
|
|
|
2017 (1)
|
|
Reproductive and social health education
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 01/01/2017
Abstract: On 6th December 2009, the Cabinet approved the PEKERTI Policy & Action Plan proposed by Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development (MWFCD), which aims to guide young people from getting involved in social problems.
|
|
|
|
2016 (1)
|
|
Investing in young people: matching education with employment needs
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2016
Abstract: Education has always been the engine of growth for Malaysia. Malaysia aspiration to become a high income nation by 2020. Multi-prong strategies which include access to education for all among the pillars to transforming the nation. Malaysia has always been embracing with the strategies and action plans of the sustainable development goals regardless of class, race, gender, age and creed.
|
|
|
|
2014 (1)
|
|
Population change and educational planning in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: Strengthen national capacity to plan and manage changing. Educational systems in response to the needs of society. Planning and preparing the education sector through long-term involvement and focused [sustainable] interventions. Improve the quality of the educational experience itself. Realise global agenda like ESD, EFA, MDGs and post-2015 Development (Education) Agenda. This presentation is describes about population change and educational planning in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
2013 (1)
|
|
Family education@LPPKN = Pendidikan kekeluargaan@LPPKN
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: The National Population and Family Board (NPFDB), agency under the Ministry of Women Family and Community Development which was initially known as the National Family Planning Board (NFPB) was established in 1966 as a statutory body. Its main objective was to implement the National Family Planning Programme but its scope has now been expanded to Population, Family Development and Reproductive Health which is in line with 1984 Amendments Act. The Malaysian family today is facing numerous challenges due to rapid socio-economic development and globalization. New challenges have emerged in the social and economic arena, which have had an impact on Malaysian families. Among the challenges experienced by the family institution are changing family structure and dynamics, balancing family and career, fulfilling economic needs parenting of young children and adolecents as well as weakening marital and family relationships. Parallel with the Government's emphasis on strengthening the family institution, the NPFDB has developed and implemented a wide range of family development programmes encompassing advocacy activities and promotion, training and education, services, research and development (R&D) as well as policy formulation. In December 2010, the Government approved the National Family Policy and its Plan of Action, thus mainstreaming the family perspective in all socio-economic planning and development.
|
|
|
|
2009 (1)
|
|
Achieving the ICPD-PoA and MDGs
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2009
Abstract: Malaysia has achieved most of the goals set in the ICPD-PoA. Other development goals included in the MDGs are in the areas of poverty reduction, universal education, reductions in maternal and child mortality, gender equality and environmental sustainability.
|
|
|
|
2004 (2)
|
|
Financial problems of university students and its relationship with academic performance
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2004
Abstract: This study that has been done in University Putra of Malaysia was to identify the relationship between financial problems and academic performance and to determine the difference in financial problems between male and female students. A total of 1,500 students who received educational loan were chosen through systematic sampling and given a self-administered questionnaire. The findings of the study revealed that financial problems were related to academic performance where the better the result, the less average number of financial problems were faced by the students. Meanwhile male students on the average have higher number of financial problems compared to female students.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financial beliefs and behaviour of college students: cultural differences
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2004
Abstract: This study compared the financial beliefs and behaviour of college students in two different cultures; Malaysia and United States. Using the social learning framework, the study assumed that children socialized in different culture will have different beliefs and behaviours. Two sets of data used were data from 665 college students Iowa State University (ISU)and convenience sampling of data from self administered questionnaires among 366 students of University Putra Malaysia (UPM). The result of the study revealed some similarity but many more differences. Cultural practices, economic and social environment influenced financial beliefs and behaviour of college students in both cultures. Service available and rules and regulations influence accessibility to services and choices available. ISU students was displaying favourable financial behaviour compared to UPM students. Students need to be aware and understand financial complexity to help them manage limited financial resources while studying as well as prepare them for work life.
|
|
|
|
2003 (1)
|
|
Population, education and development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2003
Abstract: Malaysia is of the view that continuous efforts in education is required to develop the individual's potential to the fullest, thus contributing to the well-being and prosperity of society and the country at large. In Malaysia, the education sector has been regarded a priority sector since our independence.
|
|
|
|
2000 (1)
|
|
Family development module for Institutions of Higher Education
Item Type: Module
Editor:
Year: 01/12/2000
Abstract: The NPFDB has initiated a family development programme (MOPKITP) for students from Institutions of Higher Education. The Family Development Module will be offered through the co-curriculum programme. This Family Development Module Package is a combination of the NPFDB's existing modules, that is Permata Kasih, Youth Exploration, SMARTbelanja, SMARTSTART, Bahtera Kasih, Belaian Kasih, Mutiara Kasih and POP Community. The outcome of this collaborative effort with the Institutions of Higher Education will be a pool of student who are "trained facilitators". Hence the NPFDB will be able to use these students to further expand its family development programmes to the grassroots.
|
|
|
|