TOPICS
Results for Topics : "Population"
|
|
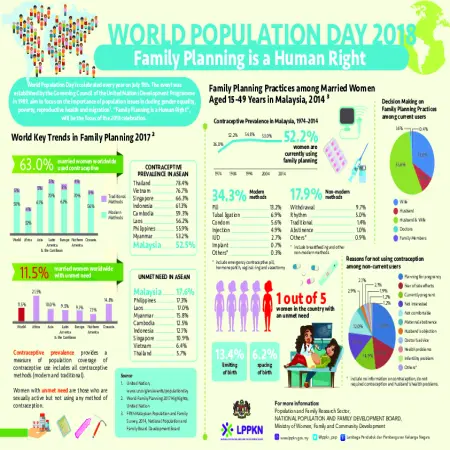
Family planning is a human right
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2018
Abstract: World Population Day is celebrated every year on July 11th. The event was established by the Governing Council of the United Nations Development Programme in 1989, aim to focus on the importance of population issues including gender equality, poverty, reproductive health and migration. Family Planning is a Human Right, will be the focus of the 2018 celebration.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family Well-Being Index Report Malaysia 2011
Item Type: Research Report
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: In the past few decades, Malaysia has and is still undergoing a process of rapid social and economic development. This is a result of policies implemented by the government such as the New Development Policy (1991-2000), National Vision Policy (2001-2010) and Government Transformation Programme (2010-2020) which all aim to transform Malaysia into a developed and competitive country. However, the processes has imposed increased demands on the family institution because of the responsibilities and the challenges faced by the family
itself. The family institution must be strengthened to offset the rapid process of social and economic development. This is important because family is the basic social unit which prepares and supplies human capital resources for national development. Given the importance of family well-being to the future of the country, a scientific study needs to be conducted to measure the level of well-being of families in Malaysia. Measuring family well-being is crucial as it can indirectly measure the impact of the implementation of national social and economic development policies on families and the extent to which the implemented policies and programmes are successful or otherwise. Hence, this study has identified suitable indicators that can provide
information about the well-being of families in Malaysia. Subsequently,
based on the identified indicators, a Family Well-Being Index (FWI) was
developed to measure the current well-being of the family as well as
to be used in policy formulation, planning for implementation of future
research, the development of new programmes and services, and
expansion of the existing programmes.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Future study- understanding the puzzling trend of high birth rate among contraceptive users in Malaysia: A case study from Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2004
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: In 1957-1966, Family Planning Association has pioneering the family planning services in most of the states of Malaysia. At that time, the family planning services were mostly available only in urban areas (NPFDB: Kuala Lumpur, Report on Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 1974). Family planning was first made as an official policy during the First Malaysia Plan in 1966, successfully through the National Planning Programme (NPP). The objectives of this study is to examine the fertility levels of respondents whose practiced family planning compared to that of who have never practiced it and this study also to study the link between socio-economic and cultural variables with those eight intermediate variables on fertility in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family well being: enhancing National Policies towards elderly parents
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Malaysia will be aged by the year 2030. The objective of National Policy for Older Persons, 2011 is to enhance the respect for and self-worth of the elderly in family, society and nation, to develop the potential of the elderly so that they remain active and productive in national development and to create opportunities for them to continue to live independently and to encourage the establishment and the provision of specific facilities to ensure the care and protection of the elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign workers in Malaysia: assessment of their economic effects and review of the policy
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study aims to help Ministry of Human Resource to better manage existing human resources in the country and to plan for the development of future human capital needs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Financing old age in a rapidly ageing high income city state: the case of Singapore
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Singapore, an affluent city state, is among the most rapidly ageing society globally. This is due to low fertility rate (TFR of 1.2 in 2011); and increasing life expectancy (18.3 years for men and 21.8 years for women at age 65 in 2011). Its support ratio (working age persons/elderly) is projected to decline from 7.9 in 2011 to 2.2 by 2030, representing a steep decline. It primarily relies on a mandatory savings tier to finance old age. This tier is administered by a statutory Board called Central Provident Fund (CPF) under the Ministry of Manpower. The CPF has over the years been used not just for retirement, but for housing health care, and other purposes. Its wide scope and mandate has resulted in considerable complexity. This paper provides an assessment of the extent to which the current old age financing arrangements are likely to address longevity, inflation, and survivors’ risks faced by individuals in their old age. Not only each person will need support for a longer period in old age, but societal and individual expectations about old age support are also changing, reflecting the affluent society.
|
|
|
|