Browse by Year
Results for Year : "2015"
2015 (33)
|
|
Tips beriadah bersama anak kecil
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2015
Abstract: Naturally little children have a wide variety. It can even dampen the atmosphere of a planned vacation. Some preparation tips can be practiced by parents before taking the child to go on vacation such as adequate and appropriate clothing, medicines, small bags, important documents, stroller and others.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lima teras keluarga bahagia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 16/11/2015
Abstract: Each of us has our own values to describe a happy family. Happiness in the family is very important and it is the goal of all of us to build family institutions. National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) has outlined five (5) Happy Family Thrusts based on the concept of KASIH, namely Love, Morality, Health, Knowledge and Harmony. Let there be different recipes and molds of pure values that are practiced in the family but the purpose is to create a happy family.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ikat anak: siksa atau keselamatan
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 10/11/2015
Abstract: The average trend in Asia, especially in Malaysia, parents prefer to hold or support the baby on the grounds that it is easier to monitor, breastfeed and put them to sleep. Many parents seem to assume that sitting on their lap is enough to protect their baby from accidents and upset to see a toddler lying tied up in a car seat. Based on statistics, the use of child safety seats and travel systems is not taken seriously by most parents in Malaysia. According to a study conducted by MIROS, babies will be thrown forward at high speeds even if held by an adult during a vehicle collision even with only 30km per hour. Most will be killed as a direct result of the impact.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Antara hak dan tanggungjawab membimbing anak bertanggungjawab
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/10/2015
Abstract: Rights can be defined as belonging to each individual while responsibilities are something that must be exercised. Kids who like to take people’s stuff have impulsive traits. Impulsive means someone who has a strong urge to have something. When the desire peaked, he had to get it right away. Some tips are shared to parents when faced with this situation such as encouraging children to ask permission every time they want to borrow items that do not belong to them, explaining to children about the difference between borrowing and taking other people's items without permission and consistent and firm in correcting actions. misconduct of children.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bijak berbelanja, keluarga bahagia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/09/2015
Abstract: Building a family requires knowledge of proper financial management. Both before and after marriage, financial problems will always linger in our minds, especially when family members are increasing. Seven (7) quick guides on family financial management using SmartBelanja Module for mutual benefit i.e. intention to save, have fixed and additional income, distribution of income money immediately for certain payments, make savings, always discuss with family members to avoid wastage and always pray that sustenance is always a blessing.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aduh! Sakit kepalaku: membimbing anak bertanggungjawab
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/08/2015
Abstract: Every child born into this world is a perfect and holy gift of God. Children are like white cloth and it is the parents who are responsible for shaping the life of their children. Every child born is in perfect condition and has great potential to be an excellent human being. Fatherhood and Motherhood The LPPKN Family@Work Module provides guidance to participants on the style of fatherhood, namely Authoritarian, Permissive, Neglect and Authoritative. The fact is, as a parent the goal is to raise children to be happy, healthy and successful.
|
|
|
|
|
|
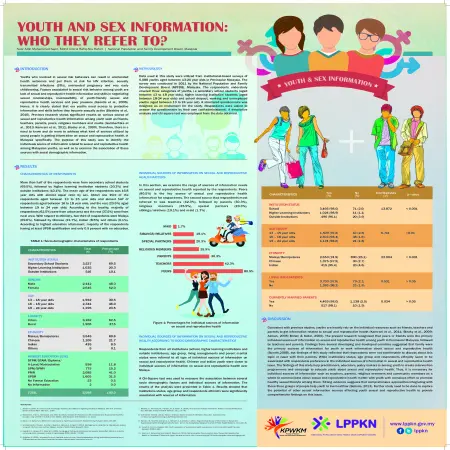
Youth and sex information: who they refer to?
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2015
Abstract: Youths who involved in sexual behaviors can result in unintended health outcomes and put them at risk for HIV infection, sexuality transmitted infections (STIs), unintended pregnancy and very early childbearing. Factors associated to sexual risk behavior among youth are lack of sexual and reproductive health information and skills in negotiating sexual relationships, inaccessibility of youth-friendly sexual and reproductive health services and peer pressure (Kaestle et Al., 2005). Hence, it is clearly stated that our youths need access to protective information and skills before they become sexually active (Bleakley et al., 2010) Previous research shows significant results on various source of sexual and reproductive health information among youth such as friends, teachers, parents, peers, religious members and media (Gombachika et al.,2013; Kamrani et al., 2011; Bleaky et al., 2009) therefore, there is a need to know and do more address what kind of sources utilized by young people in getting information on sexual and reproductive health, in Malaysia specifically. The purpose of this study was to identify the individuals source of information related to sexual and reproductive health among Malaysia youth, as well as to examine the association of these sources with social demographic information.
|
|
|
|
|
|
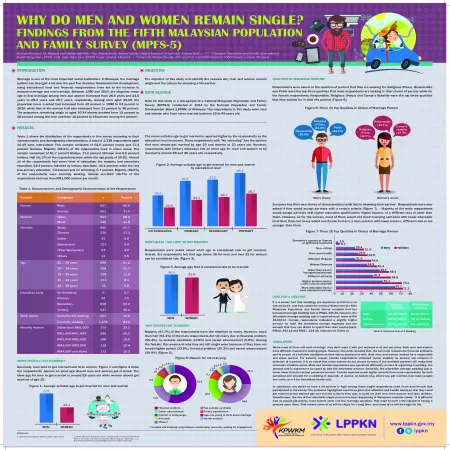
Why do men and women remain single? Findings from the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5)
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 01/07/2015
Abstract: Marriage is one of the most important social institutions. In Malaysia, the marriage pattern has changed a lot over the past few decades. Socioeconomic development, rising educational level and financial independence have led to the increase in delayed marriage and non-marriage. Between 1980 and 2010, the singulate mean age at first marriage among men and women increased from 26.6 years and 23.5 years to 28.0 years and 25.7 years, respectively. Among men aged 25-29, the proportion never married had increased from 40 percent in 1980 to 53 percent in 2010, while that of the women had also increased from 21 percent to 38 percent. The proportion remaining single at aged 30-34 almost doubled from 15 percent to 28 percent among the men and from 10 percent to 18 percent among the women. The objective of this study is to identify the reasons why men and women remain single and the criteria for choosing a life partner.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yang mana satu pilihan: keluarga kecil atau besar
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 10/07/2015
Abstract: In the current of modernization, many couples are planning to limit the number of their family members. Among the factors that push them to plan a family are getting married at a late age and the rising cost of living. The practice of family planning is very helpful in determining the birth distance between children and the size of the appropriate number of children for a family. This contraceptive practice can also prevent pregnancy in high-risk women, i.e. women with serious health problems or hereditary diseases.
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 tips luangkan masa berkualiti bersama keluarga
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 03/06/2015
Abstract: Quality time with family is when family members can spend time with mutual benefits. The time is filled with activities or interactions that can further strengthen the relationship between family members. This article shares about 10 tips to spend quality time with family such as, praying together, eating, tidying and cleaning the house together, studying children's lessons, shopping, doing leisure activities together, traveling, family reunions, doing hobbies together, and corner mini library.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Toleh kiri dan toleh kanan
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2015
Abstract: The aspect of safety in the family needs to be educated and made a daily practice and needs to be educated with patience without despair. There are some simple tips to practice in family safety such as don’t stop praying, keep dangerous and important equipment in a special place, safe zone to explore and consensus brings blessings.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Imbangi keluarga dan kerjaya
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2015
Abstract: Based on the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-4), it was found that overall, mothers do more leisure activities with their children, especially children under seven years old. This study found that the percentage of parents who often spend special time with their children is higher among mothers (80.2%) than fathers (65.3%). However, the percentage of those who frequently took their children on outings was almost the same between mothers (52.2%) and fathers (52.4%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apa wanita perlu tahu: subur@tidak subur?
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2015
Abstract: Fertility is the ability to conceive naturally. As a measure, fertility rate is the number of children born per individual, household or population. Fertility varies according to fertility, i.e. the potential to reproduce (which is influenced by gamete production, fertilization and the ability to conceive long enough). There are several types of ovulation disorders that are 35% of the cause of infertility in women, namely anovulation. Anovulation is a condition where no ovulation process occurs or the egg process is released from the ovaries, oligovulation is an irregular ovulation process that sometimes occurs, sometimes not and the anovulation cycle is a menstrual cycle in which no ovulation process occurs at the cycle.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selamatkah mainan anak anda?
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/04/2015
Abstract: Children's toy can help the educational and developmental process of children at an early age. However, the selection of children's toys needs to be done wisely especially if it involves safety aspects. If parents do not carefully choose toys, it can invite danger to the safety of children. To ensure the safety of children and prevent accidents or unwanted incidents, some things that need to be considered include choosing toys according to the level of age suitability of children, toys not made of toxic materials, avoid toys that contain magnetic materials or batteries to little children and toys that have noise.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Portrait of 1Malaysia Family First (1MFF)
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2015
Abstract: The 1MFF movement is a national agenda to increase commitment and invite all levels of society to return to giving priority to the family institution in all efforts, planning and actions. It is hoped that the 1Malaysia Family First (1MFF) element will create a lasting bond of love in family and community institutions. The initiatives introduced under the 1MFF Movement are implemented based on the 3 thrusts outlined in the National Family Policy, namely to increase the commitment and social responsibility of all parties in implementing family -friendly policies and programs; review and ensure existing laws, policies and regulations prioritize the family perspective; and provide family services and facilities that are easily accessible and accessible to families.
|
|
|
|
|
|
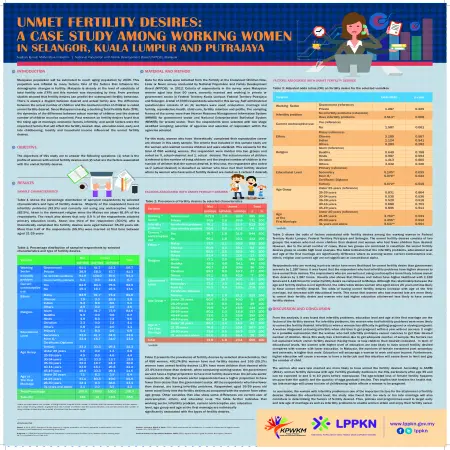
Unmet fertility desires: a case study among working women in Selangor, Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia population will be estimated to reach aging population by 2035. This projection was inflated by many factors. One of the factors that influence the demographic changes is fertility. Malaysia is already at the level of substitute of total fertility rate (TFR) and this number was decreasing by time. From previous studies showed that fertility desires can predict the subsequent fertility behavior. There is always a disjoint between desired and actual family size. The difference between the actual number of children and the desired number of children is called unmet fertility desired. Since Malaysia is having a declining Total Fertility Rate (TFR), the dynamics of the difference between actual number of children and the desired number of children must be examined. Past research on fertility desires found that the rising age at marriage, economic factors, infertility, and social factors were the important factors that will affect the fertility desired. Also, education level, early and late childbearing, locality and household income influenced the unmet fertility desires.
|
|
|
|
|
|
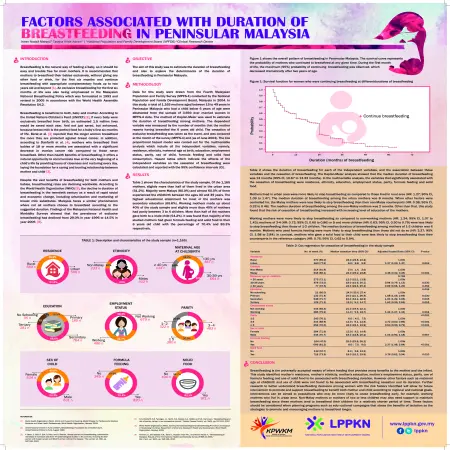
Factors associated with duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breastfeeding is the natural way of feeding a baby, so it should be easy and trouble free for most mothers. It is recommended that mothers to breastfeed their babies exclusively, without giving any other food or drink, for the first six months and continue breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods up to two years old and beyond [1]. An exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life was also being emphasized in the Malaysian National Breastfeeding Policy which was formulated in 1993 and revised in 2005 in accordance with the World Health Assembly Resolution 54.2. Breastfeeding is beneficial to both, baby and mother. According to the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) [2], if every baby were exclusively breastfed from birth, an estimated 1.5 million lives would be saved each year. And not just saved, but enhanced, because breast milk is the perfect food for a baby’s first six months of life. Beral et al. [3] reported that the longer women breastfeed the more they are protected against breast cancer. In addition, according to Danforth et al. [4], mothers who breastfeed their babies of 18 or more months are associated with a significant decrease in ovarian cancer risk compared to those never breastfeed. Other than health benefits of breastfeeding, it offers a natural opportunity to communicate love at the very beginning of a child’s life by providing hours of closeness and nurturing every day, laying the foundation for a caring and trusting relationship between mother and child [2]. Despite the vast benefits of breastfeeding for both mothers and babies, breastfeeding rates are declining worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [5], the decline in duration of breastfeeding in the twentieth century as a result of rapid social and economic change, including urbanization and marketing of breast milk substitutes. Malaysia faces a similar phenomenon where not all mothers choose to breastfeed according to the suggested duration. Findings of the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Surveys showed that the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding had declined from 29.0 % in year 1996 to 14.5 % in year 2006 [6]. Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the duration of breastfeeding and also to explore the determinants of the duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sosialisasi dan kawalan sosial dalam kehidupan remaja berisiko: kajian kes di projek Perumahan Rakyat (PPR) Sri Pahang, Bangsar dan Sri Pantai, Lembah Pantai, Kuala Lumpur
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: This study focused on a group of adolescents categorized as adolescents at risk in the People's Housing Project (PPR) area in urban areas. Purpose of the study is to identify and understand the life patterns of at -risk adolescents includes their involvement in deviant behavior, the role of socialization agents and forms of social control in the lives of at -risk adolescents. This study uses design qualitative form using in -depth interview and observation methods did not participate. A total of 10 teenagers consisted of six boys and four women aged between 16 to 22 years from PPR Sri Pahang, Bangsar and PPR Sri Pantai, Lembah Pantai have been purposefully selected.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gaya hidup wanita dan faktor risiko kanser payudara: satu kajian literatur
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breast cancer is currently the most common cancer in women worldwide. It is said that there is no proven method of preventing cancer. However, studies have shown that there are some women’s lifestyle factors that have been scientifically shown to increase the risk of breast cancer. A review of the literature from the epidemiological, medical, and psychosocial disciplines strives to analyse factors that tend to increase the risk of developing breast cancer. Published material reviewed concerning the connection between breast cancer risk and lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity. This review shows that several women’s
lifestyle factors have been regularly considered as risk factors for developing breast cancer. They include women who have not had children or women who had their first child at an older age, short duration of brestfeeding or not breastfeed at all, diet and nutrition, and psychological stress.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adolescent perception on family well-being: the effect of family economic status, family functioning, and community support
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The objective of this presentation is to examine the difference of family well-being across several demographic information and to examine the relations between the family well-being in adolescents perceived family economic status, quality of family functioning, and community and neighbourhood support.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Highlights of family and social issues : Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS 5-2014)
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: This slide Highlights of Family and Social Issues from finding of the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS 5-2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mammogram Screening Subsidy: Program in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: In Malaysia, a woman has a 1:19 life time risk of developing breast cancer in her lifetime. Breast cancer contributes 32.3% of all female cancers. To reduce the incidence of breast cancer, the Government has embarked on the subsidised Mammogram Screening Program. This aims at promoting greater awareness and encouraging women to undergo mammogram screening for early detection of breast cancer. The objective of this subsidy is to promote greater awareness on breast cancer and the importance of breast examination.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nuptiality, fertility and contraceptive use: preliminary findings from the 5th Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS -5)
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The current marital trend status shows more than 90 % are currently married while the percentage of divorce or separation is increasing. Next, current marital status by age group in 2014 showed that 93.1 % is currently married and 5.3 % among women 20-24 are divorce or separated. This paper discuss about nuptiality, fertility and contraceptive use from preliminary finding of the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5) 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measuring Malaysian well-being through the personal well-being index (PWI): findings from the fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2014
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The aim of this study is to measure the well-being of Malaysian population through the use of PWI scale developed by the International Wellbeing Group (IWbG). Responses on the PWI scale were collected from over 10,000 adults aged 18 to 59 drawn from a sample of 18,852 living quarters throughout the country. Through the MPFS-5, the Personal Well-Being Index for the Malaysian was recorded at 7.71 out of a maximum score of 10. Out of the eight domains identified, the Spirituality or Religion domain recorded the highest score of 7.56. It then followed by the domain scores of Personal Relationships (7.54), Community-Connectedness (7.52), Personal Safety (7.35), Personal Health (7.10), Future Security (6.96), Standard of Living (6.58) and Achieving in Life (6.56).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prevalence and risk factors of pregnancy loss in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The objective of this paper is to study the prevalence and risk factors of pregnancy loss in Malaysia. The risk of pregnancy loss is highest among Indian, followed by Malay and Chinese. The risk of pregnancy loss increases with level of education, age at 1st marriage and number of previous non-live births.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Household chores and your child
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Getting your child to help out with household chores on a regular basis can be beneficial for him to grow into a successful adult. This is due to a sense of self-worth and competency, and he will also be more responsible in other aspects of his life. Another benefit is that he will be more likely to have better self-esteem and it also makes him feel like a part of the family.Indirectly, this will teach him about the importance of family responsibility.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parent's role in preventing teen pregnancy
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines teenage pregnancy as a ‘teenaged or underaged girl (within the ages of 15–19) becoming pregnant.’ However, the term teenage pregnancy is often used in our society to mean unmarried adolescent girls who become pregnant. In many cultures and communities including Malaysia, this carries a social stigma.
Pregnant teenagers also face many additional obstetric, medical & social issues compared to women who give birth in their 20’s and 30’s.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Realizing the future we want: integrating population issues into sustainable development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia is closely monitoring the developments and discussion on the post-2015 development agenda. Malaysia believes that the post-2015 development agenda should integrate existing international commitments and outcomes of UN conferences and deliver on equality, social inclusion, decent work, and sustainable livelihoods.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balancing the three dimensions of sustainable development: from integration to implementation
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia has been able to transform from a low-income economy in the 1970s to a high middle-income economy today. Parallel to the economic achievement, Malaysia has also achieved commendable success in terms of social progress. These achievements are in line with Malaysia’s commitment to place the wellbeing of the people as the priority of its development efforts. As such, the government is committed to protect the environmental quality of life and caring for the planet, while harnessing economic value from the process.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Faktor risiko dan pelindung terhadap kesihatan seksual dan reproduktif remaja di Semenanjung Malaysia
Item Type: Research Report
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: In Malaysia, statistics from the National Registration Department (NRD) show that a total of 214,033 illegitimate children were born from 2004 to 2009. While statistics from the Royal Malaysia Police (RMP) show that 596 cases of baby abandonment were reported from 2005 to 2013. For the total number of rape crimes in among teenagers under the age of 18, PDRM statistics show an increase from 1,710 cases in 2006 to 2,658 cases in 2013. The increase in such cases shows that today's teenagers face the problem of moral decay and fragility of identity which is a concern of Malaysian society. Accordingly, knowledge of sexual and reproductive health can help adolescents avoid negative symptoms such as cases of extramarital pregnancies and social symptoms related to sexuality. The objective of this study was to (i). to study the prevalence of unhealthy sexual behavior among adolescents aged 13-24 years in peninsular Malaysia; (ii). identify risk factors related to adolescent sexual and reproductive health (ASRH); and (iii). identify protective factors related to ASRH. This study was implemented using two (2) main approaches, namely quantitative and qualitative methods. The design of the quantitative study was successfully conducted on 5,088 adolescents aged 13 to 24 years. The qualitative study involved a total of eight (8) Focus Group Discussions (FGD) conducted in eight (8) selected detention centers and shelter hostels located in several states in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family Well-Being Index Report Malaysia 2011
Item Type: Research Report
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: In the past few decades, Malaysia has and is still undergoing a process of rapid social and economic development. This is a result of policies implemented by the government such as the New Development Policy (1991-2000), National Vision Policy (2001-2010) and Government Transformation Programme (2010-2020) which all aim to transform Malaysia into a developed and competitive country. However, the processes has imposed increased demands on the family institution because of the responsibilities and the challenges faced by the family
itself. The family institution must be strengthened to offset the rapid process of social and economic development. This is important because family is the basic social unit which prepares and supplies human capital resources for national development. Given the importance of family well-being to the future of the country, a scientific study needs to be conducted to measure the level of well-being of families in Malaysia. Measuring family well-being is crucial as it can indirectly measure the impact of the implementation of national social and economic development policies on families and the extent to which the implemented policies and programmes are successful or otherwise. Hence, this study has identified suitable indicators that can provide
information about the well-being of families in Malaysia. Subsequently,
based on the identified indicators, a Family Well-Being Index (FWI) was
developed to measure the current well-being of the family as well as
to be used in policy formulation, planning for implementation of future
research, the development of new programmes and services, and
expansion of the existing programmes.
|
|
|
|