Browse by Year
Results for Year : "2013"
Annual Report (1)
Article (3)
|
|
Ethnicity and support for parents in Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2013
Abstract: This study analyzed support as reported by adult women to parents and parents-in-law in a multi-ethnic setting. It examined ethnic diversity and other influencing factors in the provision of support. Data utilized came from the Women sample of the 2004 Malaysian Population and Family Survey and was filtered to include the three largest ethnic groups in Malaysia- Malays, Chinesse and Indians.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socio-economic determinants of pap smear screening among married women in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/02/2013
Abstract: This study is to identify the influences of socio-economic factors towards the practice of Pap smear screening among ever married women. Bivariate correlations and logistic regression analysis was applied to the data set containing 3,283 ever married women age 15-49 years, interviewed during the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey, 2004. It was found that only half the women had undergone Pap smear screening prior three years of survey, in which Chinese had the highest percentage of Pap smear screening. The logistic statistical analysis also had identified several variables has important determinant has of Pap smear screening for ever married women. Finding from this study suggest a significant relationship between the cervical cancer awareness and knowledge, age and ethnicity for those women who practice Pap smear screening.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Factors influencing family life satisfaction among parents in Malaysia: the structural equation modeling approach (SEM))
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: The study attempts to investigate the factors that influence family life satisfaction (FLS) among parents in Malaysia. The study modeled the variable of parental involvement, family functioning, family resilience and time with family as independent constructs. Data for the study was gathered from nationally representative survey of “Family Well-Being Index” study conducted by National Population and Family Development Board Malaysia. Response from 2808 sampled households which involved about 1484 (52.8%) fathers and 1324 (47.2%) mothers of having a child aged at least 13 years old were utilized for the purpose of the current study. A Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed by using Analysis of Moment Structure (AMOS) software. The study found all the modeled independent constructs tested had a significant and direct influence on family life satisfaction among the respondents except for parental involvement construct. The findings of the study suggests that some improvement should be made for the parental involvement constructs which covers different aspects of family life satisfaction which will lead the measurement model be more heterogeneous.
|
|
|
|
Book (1)
|
|
Family education@LPPKN = Pendidikan kekeluargaan@LPPKN
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: The National Population and Family Board (NPFDB), agency under the Ministry of Women Family and Community Development which was initially known as the National Family Planning Board (NFPB) was established in 1966 as a statutory body. Its main objective was to implement the National Family Planning Programme but its scope has now been expanded to Population, Family Development and Reproductive Health which is in line with 1984 Amendments Act. The Malaysian family today is facing numerous challenges due to rapid socio-economic development and globalization. New challenges have emerged in the social and economic arena, which have had an impact on Malaysian families. Among the challenges experienced by the family institution are changing family structure and dynamics, balancing family and career, fulfilling economic needs parenting of young children and adolecents as well as weakening marital and family relationships. Parallel with the Government's emphasis on strengthening the family institution, the NPFDB has developed and implemented a wide range of family development programmes encompassing advocacy activities and promotion, training and education, services, research and development (R&D) as well as policy formulation. In December 2010, the Government approved the National Family Policy and its Plan of Action, thus mainstreaming the family perspective in all socio-economic planning and development.
|
|
|
|
Conference or Workshop Item (13)
|
|
Pendekatan sokongan keluarga dalam kalangan penjaga warga tua: pengetahuan, kemahiran dan kesejahteraan
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study is conducted in line with global development (modernization) the impact on the care of elderly parents in their own (informal) families is declining and may worsen in the future. This phenomenon does not only occur in Malaysia but it is a global issue especially in developed and developing countries. Among the causes of this phenomenon are due to the increase in life expectancy of elderly parents (Department of Statistics Malaysia, 2000), the effects of modernization and changes in family structure, increase in divorce rates, reduction in birth rates, geographical movements and globalization.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Emerging patterns of Indonesia's international population mobility
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This paper attempts to examine some new trends in Indonesia’s international migration, both out-migration from and in-migration to Indonesia. More and more Indonesians have moved to other countries to pursue higher education, job opportunities and to settle down. On the other hand, rapid economic growth and the large consumer market have attracted increasing number of foreigners to work and invest in Indonesia. International population mobility is becoming a more important demographic process, with profound ramifications on economic development in Indonesia and other countries, in ASEAN and beyond.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Migration in Malaysia: social and family impact
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This paper highlights the key findings from surveys done by the Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development (MWFCD) and the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB). The Survey on the Implications of Employing Foreign Domestic Helpers (FDH) on the Family Institution in Malaysia was conducted by the MWFCD in 2009. The study found that many families rely on FDH for child care and domestic work. Some of the families find that having a FDH has a negative effect on their family relationships while some have no problems with it. The study on Indonesian Migrants in Tawau, Sabah conducted by the NPFDB in 2010 found that the local community in Sabah felt that the presence of Indonesian migrants in their community had both positive and negative effects. The effects of migrants were studied from the perspective of economy, education, health, safety, culture, housing and neighbourhood.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Immigration to the United States: recent trends and future prospects
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: The United States is popularly known as a “nation of immigrants.” For recent immigrants and their descendants, this term means that they belong part of a long tradition of peoples who came the United States seeking economic opportunity, fleeing injustice or oppression in their homeland, and a better life for their children. Long term residents of the United States, those who immigration experience is several generations in the past, often have mixed feelings about new immigrants. They may be very proud of their immigrant forbearers from Italy, Poland, or Ireland, but this historical experience does not always generate sympathy for recent arrivals. They often think the new immigrants are somehow different and less deserving than those who arrived in the past. These beliefs about new immigrants are based on assumptions of difference--the recent newcomers have a different religion, a different language, or are from a different country that will make them less likely to assimilate to American society and culture. Then, there is a significant proportion of Americans are strongly hostile to new immigrants – they would like to stop all immigration and even to expel those who are already here, including the estimated 12 million immigrants who do not have any legal standing to be in the US. This ambivalence about immigration, and even hostility to immigrants, is part of the fabric of American society, past and present. Immigrants from around the world have been coming to the United States in large numbers for almost 4 centuries, long before the founding of the nation in 1787. Although immigrants are often welcomed, particularly by family and friends from their homeland, they often encounter indifference and occasional prejudice from long resident Americans. In this overview, I survey the trends in immigration to the United States with a focus on the most recent period. Current levels of immigration are very high, but relative the national population. In fact, the portion of the US population that is foreign born (or the children of the foreign born) was even higher during the first decade of the 20th century and during the 1840s and 1850s. These earlier waves of mass migration generated an extreme levels of American nativism that were much hostile than those at present. There was a significant number of Chinese, Japanese and Filipino immigrants in the late 19th and early 20th century, but the majority originated in Europe. At present, about half of new immigrants come from Mexico and other Latin American countries, and about one-quarter come from Asia, including China, India, Vietnam, and the Philippines. In the 1970s and 1980s, most immigrants settled a few states, particularly California, New York, Texas, Florida, and Illinois. In the 1990s, immigrants spread out to “new destinations,” including small towns and cities in the South and Midwest. They are not the poorest of the poor. Some immigrants arrive with very high educational credentials and play a disproportionate role in the American high tech sector. In general, the children of immigrants do very well in American society, both educationally and economically. Immigrants and their children are also distinctive in terms of their determination to succeed. Of course, not all immigrants are successful. Some join gangs and experience downward mobility. They may even adopt attitudes that reject the goal of social mobility. But, all in all, most empirical research shows that contemporary immigrants are making a positive contribution to American society, just as earlier waves of immigrants did.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Growth of urban towns in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Malaysia has experienced an outstanding growth of urban towns since its formation in 1963. The shift from agricultural to an industrial based economy has inevitably led to rapid physical, social and economic changes. The impact of urban spatial transformation accentuated the growth in the number of urban towns with urban centres increasing in size and expansion of major towns outwards to sprawl into peripheries. This paper highlights the growth of urban towns in Malaysia based on the data available from the 1970, 1980, 1991, 2000 and 2010 Population and Housing Censuses. The data reveals a surge of growth in number from 72 towns in 1980 to 228 towns in 2010. The increase in the growth of urban centres and the urbanization process is the result of spatial transformation, demographic phenomenon and various government measures for a measureable balanced development.
|
|
|
|
|
|
International migration between ASEAN Australia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: International migration is an increasing influence in ASEAN. The 2013 United Nations Population Report indicates that ASEAN had the third fastest growing international migration currently of all world regions over the 2000-13 period. This presentation examines the global context in which this increase in mobility is occurring. It summarises the main elements in this increased importance of migration. It focuses then on recent developments in the migration relationship with Australia. Australian international migration data is of very high quality and allows the movement between ASEAN countries and Australia to be qualified. It detects permanent immigration and emigration as well as non-permanent moves. It is demonstrated that the migration relationship between ASEAN and Australia is emphatically an interacting one. It is a system rather than a south-north movement. The characteristics of migrants are examined and issues of brain drain addressed. The paper considers some policy dimensions of the migration relationship for development in ASEAN.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Family well being: enhancing National Policies towards elderly parents
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Malaysia will be aged by the year 2030. The objective of National Policy for Older Persons, 2011 is to enhance the respect for and self-worth of the elderly in family, society and nation, to develop the potential of the elderly so that they remain active and productive in national development and to create opportunities for them to continue to live independently and to encourage the establishment and the provision of specific facilities to ensure the care and protection of the elderly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current trends in transnational population flows in Malaysia: Issues, policy and challenges
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: In the last 40 years there has seen a substantial increase in Malaysia’s foreign pop. According to the last National Census in 2010, out of a pop of 28.4 million, over 8.3% are non-citizens. The increase is mainly the result of labour inflow since the early 1970s due to Malaysia’s relatively better economic development and political stability which attract economic migrants and asylum seekers from within and outside the ASEAN region. This paper which focuses on current transnational flows in the country has the following objectives: 1. To provide an overview of transnational population flows in Malaysia in the last decade and identify major streams that are causing considerable concern to the state and the Malaysian public. The focus is on the low skill foreign workers, the largest category of migrants in Malaysia. 2. To examine public perceptions of foreign workers, how such perceptions are formed and what their impacts are on state policy. 3. To discuss the state policy on foreign workers, both legal and irregular, the objective of the policy and its strategies. 4. To highlight the challenges faced by the state in implementing the foreign worker policy. 5. To evaluate the achievement and shortcomings of the policy. The writer identifies five types of transnational inflows into Malaysia i.e. that of low skill migrant workers both legal and irregular; asylum seekers; expatriates; foreign students; and participants of Malaysia’s My Second Home (MM2H) project.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal migration and socio-demographic changes in Malaysia
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This paper re-examines the levels, trends and patterns of internal migration, followed by some discussions on the causes and consequences of internal migration in Malaysia in 1991 and 2000. A more up to date analysis awaits the release of migration data from the 2010 census. The focus of this paper is on inter-state and inter-regional rather than intra-state migration as more people moved across states than within state. Key questions to be addressed include the reasons for the high concentration of migration in the Klang Valley since the 1970s, migration selectivity in terms of age, education and ethnicity. The migration impact on socio-demographic changes and policy issues will also be examined.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign workers in Malaysia: assessment of their economic effects and review of the policy
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study aims to help Ministry of Human Resource to better manage existing human resources in the country and to plan for the development of future human capital needs.
|
|
|
|
Infographic (1)
Newsletter (1)
|
|
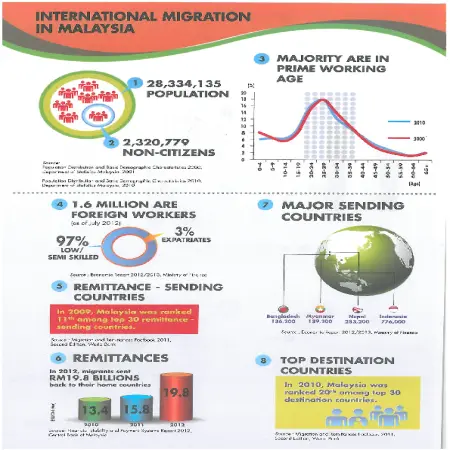
New trends in migration: demographic aspects
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Industrialization has brought about rapid urbanization with about 7 in 10 Malaysians now residing in cities. Industrialization has also resulted in Malaysia being an attractive destination for migrants. Based on Migration and Remittances Factbook 2011 produced by World Bank, Malaysia was one of the top 30 countries in terms of number of immigrants flowing into the country in 2010. According to Census 2010, there were 2.3 million non-citizens residing in Malaysia. The majority of migrants are in the age group of ' high economic activity'. They are mainly employed in the manufacturing, agricultural and construction sectors. Employers prefer hiring foreign workers due to their willingness to work extra hours and for their relatively lower wages.
|
|
|
|
Report (1)
Scientific Poster (1)
|
|
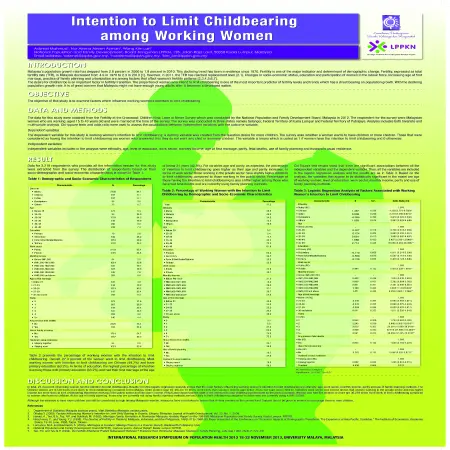
Intention to limit childbearing among working women
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2013
Abstract: Malaysia's population growth the rate has dropped from 2.6 percent in 2000 to 1.9 percent in 2010. This declining trends has been in evidence since 1970. Fertility is one of the major indicator and determinant of demographic change. Fertility, expressed as total fertility rate (TFR), in Malaysia decreased from 4.9 in 1970 to 2.3 in 2010. However, in 2011, the TFR has reached replacement level (2.1). Changes in socio-economic status, education and participation of women in the labour force, increasing age at first marriage, practice of family planning and urbanization are among factors that affect women's fertility pattern.
|
|
|
|
Thesis (1)
|
|
Antara dua dunia : memahami pengalaman subjektif transeksual
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: This study was designed to make a better understanding of transsexual’s subjective experiences. Semi structure face to face interview method was chosen in order to gather these data. There are three respondent (transsexual male to female) aged 30th , 40th
and 50th involved in this study, which was represented by one person for each group. The data gathered was analyzed based on topics and subtopics. Three (3) main topic such as background, experience in childhood and adolescent and self-concept was highlighted in
this study. There are numbers of interesting findings based on background, trigger that cause transsexual identity, colleague influential, emotion and behavior. These key elements should be considered directly or indirectly in order to implement policy, intervention, program and counseling. By understanding their experience well, would help enhancing their resilient and coping skills with regards to immoral activities and make them feel part of the community. This study is a prelude to other studies involving the transsexual especially for parents who have child which is tend to develop transsexual identity and other aspects such as sexual life, psychology resiliency, coping skills and ets.
|
|
|
|