Browse by Type
Results for Item type : "Scientific Poster"
2021 (4)
|
|
Source of sexual and reproductive health (SRH) information among youths in Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: A majority of respondents agreed that they sought for information on puberty topics and pregnancy to the teachers and mother as compared with other sources. While, peers and media were the second and third sources on sexual topics after teachers. However, the main sources of information on contraception were teachers and media instead of mother and father or siblings.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Achievement of desired fertility in Malaysia and association with sociodemographic characteristics
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: This study aims to examine the patterns of desired fertility achievement and the differences according to socio - demographic characteristics among married women.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Socio economics factors that effect work life balance among women in Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: This paper seeks to determine the factors that influence work life balance among women in Malaysia. This is explored with regard to whether the factors recorded affect the work life balance among women in Malaysia. The scope of the study will be concentrated toward married working women aged from 15 to 59. This paper finally concludes with discussion on the alternatives that women in Malaysia can take to get a better work life balance.
|
|
|
|
|
|
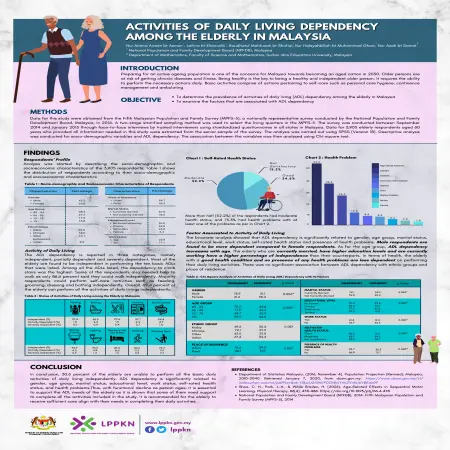
Activities of daily living dependency among the elderly in Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2021
Abstract: The objective of this study is to determine the prevalence of activities of daily living (ADL) dependency among the elderly in Malaysia and to examine the factors that are associated with ADL dependency.
|
|
|
|
2015 (4)
|
|
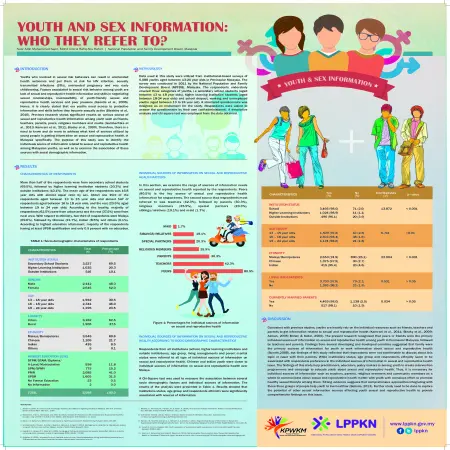
Youth and sex information: who they refer to?
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/07/2015
Abstract: Youths who involved in sexual behaviors can result in unintended health outcomes and put them at risk for HIV infection, sexuality transmitted infections (STIs), unintended pregnancy and very early childbearing. Factors associated to sexual risk behavior among youth are lack of sexual and reproductive health information and skills in negotiating sexual relationships, inaccessibility of youth-friendly sexual and reproductive health services and peer pressure (Kaestle et Al., 2005). Hence, it is clearly stated that our youths need access to protective information and skills before they become sexually active (Bleakley et al., 2010) Previous research shows significant results on various source of sexual and reproductive health information among youth such as friends, teachers, parents, peers, religious members and media (Gombachika et al.,2013; Kamrani et al., 2011; Bleaky et al., 2009) therefore, there is a need to know and do more address what kind of sources utilized by young people in getting information on sexual and reproductive health, in Malaysia specifically. The purpose of this study was to identify the individuals source of information related to sexual and reproductive health among Malaysia youth, as well as to examine the association of these sources with social demographic information.
|
|
|
|
|
|
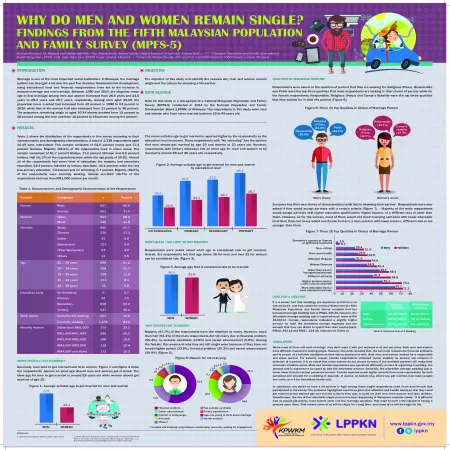
Why do men and women remain single? Findings from the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5)
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 01/07/2015
Abstract: Marriage is one of the most important social institutions. In Malaysia, the marriage pattern has changed a lot over the past few decades. Socioeconomic development, rising educational level and financial independence have led to the increase in delayed marriage and non-marriage. Between 1980 and 2010, the singulate mean age at first marriage among men and women increased from 26.6 years and 23.5 years to 28.0 years and 25.7 years, respectively. Among men aged 25-29, the proportion never married had increased from 40 percent in 1980 to 53 percent in 2010, while that of the women had also increased from 21 percent to 38 percent. The proportion remaining single at aged 30-34 almost doubled from 15 percent to 28 percent among the men and from 10 percent to 18 percent among the women. The objective of this study is to identify the reasons why men and women remain single and the criteria for choosing a life partner.
|
|
|
|
|
|
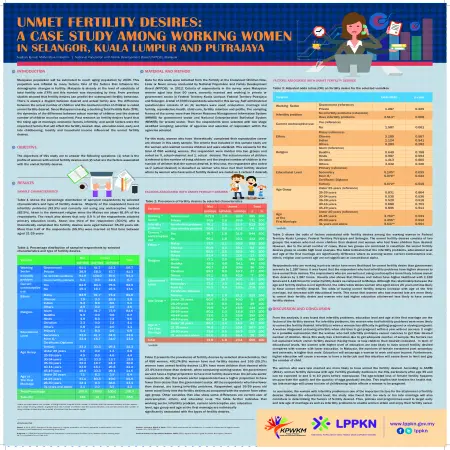
Unmet fertility desires: a case study among working women in Selangor, Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia population will be estimated to reach aging population by 2035. This projection was inflated by many factors. One of the factors that influence the demographic changes is fertility. Malaysia is already at the level of substitute of total fertility rate (TFR) and this number was decreasing by time. From previous studies showed that fertility desires can predict the subsequent fertility behavior. There is always a disjoint between desired and actual family size. The difference between the actual number of children and the desired number of children is called unmet fertility desired. Since Malaysia is having a declining Total Fertility Rate (TFR), the dynamics of the difference between actual number of children and the desired number of children must be examined. Past research on fertility desires found that the rising age at marriage, economic factors, infertility, and social factors were the important factors that will affect the fertility desired. Also, education level, early and late childbearing, locality and household income influenced the unmet fertility desires.
|
|
|
|
|
|
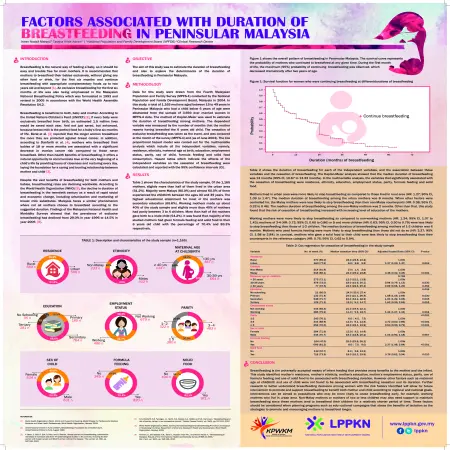
Factors associated with duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breastfeeding is the natural way of feeding a baby, so it should be easy and trouble free for most mothers. It is recommended that mothers to breastfeed their babies exclusively, without giving any other food or drink, for the first six months and continue breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods up to two years old and beyond [1]. An exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life was also being emphasized in the Malaysian National Breastfeeding Policy which was formulated in 1993 and revised in 2005 in accordance with the World Health Assembly Resolution 54.2. Breastfeeding is beneficial to both, baby and mother. According to the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) [2], if every baby were exclusively breastfed from birth, an estimated 1.5 million lives would be saved each year. And not just saved, but enhanced, because breast milk is the perfect food for a baby’s first six months of life. Beral et al. [3] reported that the longer women breastfeed the more they are protected against breast cancer. In addition, according to Danforth et al. [4], mothers who breastfeed their babies of 18 or more months are associated with a significant decrease in ovarian cancer risk compared to those never breastfeed. Other than health benefits of breastfeeding, it offers a natural opportunity to communicate love at the very beginning of a child’s life by providing hours of closeness and nurturing every day, laying the foundation for a caring and trusting relationship between mother and child [2]. Despite the vast benefits of breastfeeding for both mothers and babies, breastfeeding rates are declining worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [5], the decline in duration of breastfeeding in the twentieth century as a result of rapid social and economic change, including urbanization and marketing of breast milk substitutes. Malaysia faces a similar phenomenon where not all mothers choose to breastfeed according to the suggested duration. Findings of the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Surveys showed that the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding had declined from 29.0 % in year 1996 to 14.5 % in year 2006 [6]. Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the duration of breastfeeding and also to explore the determinants of the duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
2014 (1)
|
|
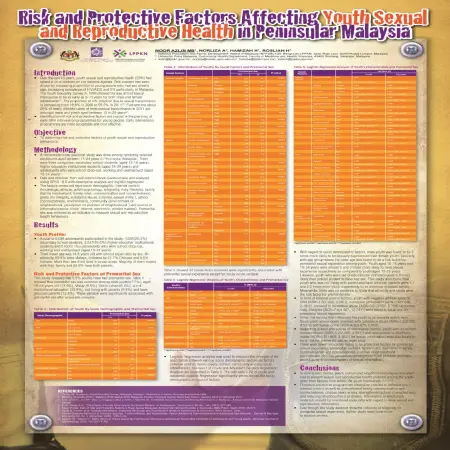
Risk and protective factors affecting youth sexual and reproductive health in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2014
Abstract: Over the last 10 years, youth sexual and reproductive health (SRH) had raised a lot of concern on the national agenda. This concern has been driven by increasing proportion of young people who had sex at early age, increasing prevalence of HIV/AIDS and STI particularly in Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
2013 (1)
|
|
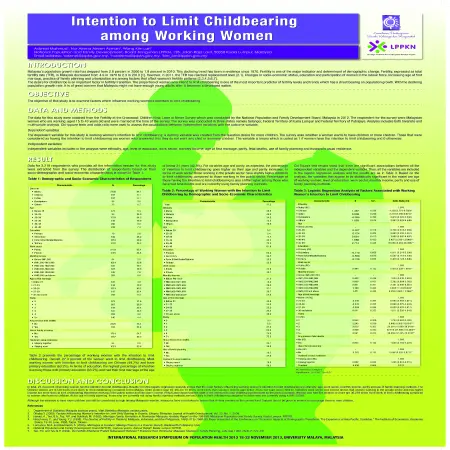
Intention to limit childbearing among working women
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2013
Abstract: Malaysia's population growth the rate has dropped from 2.6 percent in 2000 to 1.9 percent in 2010. This declining trends has been in evidence since 1970. Fertility is one of the major indicator and determinant of demographic change. Fertility, expressed as total fertility rate (TFR), in Malaysia decreased from 4.9 in 1970 to 2.3 in 2010. However, in 2011, the TFR has reached replacement level (2.1). Changes in socio-economic status, education and participation of women in the labour force, increasing age at first marriage, practice of family planning and urbanization are among factors that affect women's fertility pattern.
|
|
|
|
2012 (2)
|
|
The impact of Indonesian migrants from the locals' perception: a study in Sabah, Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/08/2012
Abstract: Being a developed country, Malaysia has been receiving a large number of labour migrants from other neighboring countries. Statistics show that the total number of non-Malaysians in 2010 is 2.3 million compared to 1.3 million in the year 2000. It is over 8 percent of the total population in Malaysia and comprises mostly of Indonesian migrants. This phenomena has a great impact on Malaysia and its people. The objective of this study is to determine the impact of Indonesian migrants from the locals' perception and also to determine if gender, ethnicity, religion, marital status, educational level, job industry and monthly income make a difference in their perception. The data used for this study were obtained from the Study on Indonesian Migrants in Tawau, Sabah conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) Malaysia in 2010. The survey managed to obtain information from 787 locals in Tawau. The dependent variable is the overall perception of the locals on the impact of the Indonesian migrants while the independent variables are gender, ethnicity, religion, marital status, educational level, job industry and monthly income. Independent t-test and analysis of variances (ANOVA) were applied to the data set. As a result, this study indicates that the locals in Tawau feel that the presence of the Indonesian migrants does have an effect on them. The mean score obtained was 95.053 out of a total of 135. The results of ANOVA showed that ethnicity (F = 6.950, df = 7), marital status (F = 12.320, df = 3), education level (F = 4.058, df = 7), job industry (F = 27.374, df = 3), and monthly income (F = 15.201, df = 6) contributed to the differences in the locals' perception on the impact of Indonesian migrants. Only gender and religion does not affect their perception. Thus, the entrance of Indonesian workers needs to be monitored as their presence are affecting the locals.
|
|
|
|
|
|
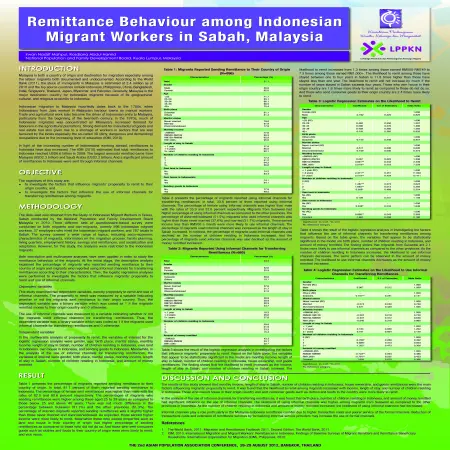
Remittance behaviour among Indonesian migrant workers in Sabah, Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/08/2012
Abstract: Malaysia is both a country of origin and destination for migration especially among the labour migrants both documented and undocumented. According to The World Bank's Migration and Remittances Factbook 2011, the stock of immigrants in Malaysia is estimated at 2.4 million as at 2010 and the top source countries include Indonesia, Philippines, China, Bangladesh, India, Singapore, Thailand, Japan, Myanmar, and Pakistan. Generally, Malaysia is the major destination country for Indonesian migrants because of its geographical, cultural, and religous proximity to Indonesia.
The objective of this study is to investigate remittance behaviour among Indonesian migrants including the decision to remit and use of informal methods of transferring remittance. The data used was obtained from the Study of Indonesian Migrant Workers in Tawau, Sabah conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board Malaysia in 2010. Three different sets of questionnaire-based survey were conducted on both migrants and non-migrants, namely 896 Indonesian migrant workers, 37 employers who hired the Indonesian migrant workers, and 787 locals in Sabah. Both descriptive and multivariate analyses have been applied in order to study the remittance behaviour of the migrants. At the initial stage, the descriptive analysis explained the percentage of migrants who send remittance and migrants who use informal channels according to their characteristics. Then, logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the factors that influence migrants' decision to send remittance and the use of informal methods of transferring remittance. The results of this study showed that age, monthly income, number of children residing in Indonesia, having own house in Indonesia and sending goods to Indonesia are the main factors contributing to the migrants' decision to remit. It was found that the likelihood to remit among migrants increased with age, income and number of children residing in Indonesia. Those who own house in their origin country and sending goods to the country are more likely to remit. In the analysis of methods of transferring remittance, it was found that birth place, number of children residing in Indonesia and the total amount of money remitted have significant relationship with the use of informal channels. The likelihood of using informal channels is higher among migrants from Sulawesi as compared to the other parts of Indonesia. As the number of children residing in Indonesia and amount of money remitted increased, the likelihood of using informal channels had decreased.
|
|
|
|