Browse by Type
|
|
Nuptiality, fertility and contraceptive use: preliminary findings from the 5th Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS -5)
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: The current marital trend status shows more than 90 % are currently married while the percentage of divorce or separation is increasing. Next, current marital status by age group in 2014 showed that 93.1 % is currently married and 5.3 % among women 20-24 are divorce or separated. This paper discuss about nuptiality, fertility and contraceptive use from preliminary finding of the Fifth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-5) 2014.
|
|
|
|
|
|
New trends in migration: demographic aspects
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2013
Abstract: Industrialization has brought about rapid urbanization with about 7 in 10 Malaysians now residing in cities. Industrialization has also resulted in Malaysia being an attractive destination for migrants. Based on Migration and Remittances Factbook 2011 produced by World Bank, Malaysia was one of the top 30 countries in terms of number of immigrants flowing into the country in 2010. According to Census 2010, there were 2.3 million non-citizens residing in Malaysia. The majority of migrants are in the age group of ' high economic activity'. They are mainly employed in the manufacturing, agricultural and construction sectors. Employers prefer hiring foreign workers due to their willingness to work extra hours and for their relatively lower wages.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nurturing healthy, happy, well-planned and empowered Filipino families: the Philippine experience
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: This paper discuss about challenges facing by Filipino families in nurturing healthy, happy, well-planned and empowered and the strategies in Philippine Development Plan 2011-2016 to overcome this problem.
|
|
|
|
|
|
National experience in population matters: adolescents and youth
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2012
Abstract: Adequate and accurate sexual and reproductive health information helps young people to make informed and responsible decisions. Howewer, cultural and religious sensitivities within the communities remain one of the major challenges in implementing reproductive health education for young people. Parents are still uncomfortable talking about reproductive health matters with their children ,leaving their children dependent upon information from their peers or other sources like the internet. The Government of Malaysia takes cognisance of the increasing importance of the sexual and reproductive health needs of adolescents and youth in Malaysia. Hence, the Government of Malaysia has put in place various policies and programmes to handle the sexual and reproductive health needs of the adolescents and youths. One of the main initiatives is the Healthy Programme without AIDS for Youth (PROSTAR). The Government of Malaysia also has established six youth-friendly adolescent centres known as kafe@TEEN to increase access to reproductive health information and services for young people aged 13 to 24 years.
|
|
|
|
|
|
National Family Policy
Item Type: Act & Policy
Editor:
Year: 00/03/2011
Abstract: Malaysia is one of the few countries that has an explicit policy on family. The National Family Policy (NFP) was launched on 19 March 2011. It advocates the concept of family wellbeing based on family values such as caring, honesty, justice and equity regardless of status, gender and age. At the macro level, the policy will be the catalyst to urge all stakeholders to take into account the family perspective in all their planning, strategy formulation or development efforts, either through their commitment, formulation or review of policies and laws that are not family friendly to ensure that programmes, services and family friendly facilities are accessible.
|
|
|
|
|
|
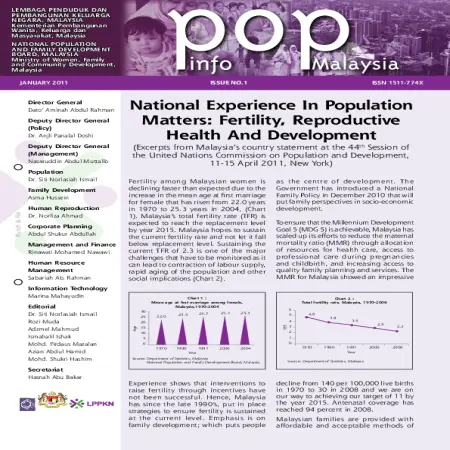
National experience in population matters : fertility, reproductive health and development
Item Type: Newsletter
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2011
Abstract: Fertility among Malaysian women is declining faster than expected due to the increase in the mean age at first marriage for female that has risen from 22.0 years in 1970 to 25.3 years in 2004. Malaysia’s total fertility rate (TFR) is expected to reach the replacement level by year 2015. Malaysia hopes to sustain the current fertility rate and not let it fall below replacement level.
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Zealand indigenous people and resilience
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2009
Abstract: Indigenous peoples throughout the world have used strengths and resiliency to preserve the ongoing effects of colonizations and as tools for sovereignty. The 'Tangata Whenua' of New Zealand, along side other indigenous and minority groups throughout the world, continue to progress the development of their own cultural frameworks and models of practice. More recently in New Zealand, particularly within the health and social services sectors, 'tangata whenua' have begun to examine resiliency research and practices which contribute to the body of knowledge in the area of 'whanau ora', and the cultural capacities and capabilities which assist families to build resiliency and protective factors and processes. This presentation examines what has been learned from the theory and practice experiences of a 'Tangata Whenua' social work practitioner and trainer.
|
|
|
|