Browse by Type
|
|
Understanding children with autism in Asean and Malaysia through a public health lens: a scoping review of current research
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/11/2025
Abstract: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition affecting approximately 1 in 100 children globally, with profound impacts across the lifespan. However. Within the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region, particularly Malaysia, systematic research on autism remains notably scarce and fragmented. This scoping review reveals critical gaps in autism research and services across ASEAN and Malaysia despite growing awareness. Prioritizing autism as a public health imperative requires commitment from researchers, policymakers, healthcare providers, educators, and communities. By committing resources to research, policy development, and service delivery, ASEAN countries can substantially improve outcomes for individuals with autism and their families.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Understanding the relationship between digital parenting styles and children’s digital resilience in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: The significant increase in online and screen time adds to the issues of children's online safety which has always posed a significant risk to parents, even before the pandemic. The opportunity given by parents to access digital gadgets has transformed how children perceive, react, and adapt to world change, especially in the era of IR4.0. Despite a huge number of studies conducted on digital media among young generations, only a few focused on digital parenting and digital resilience topics, especially in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Using games to stimulate and motivate Esl students in Malaysia
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Vocabulary is a vital part of English second language education. Unfortunately, the teaching and learning process is challenging for students as regular classroom activities have become tedious and boring, which does not motivate them to learn. Not only that, but this also discourages them from practising outside of the classroom. To help encourage students to become more motivated in learning and improving their English vocabulary, teachers need to consider more creative activities to be used in the classroom.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unleashing teen pregnancy in Malaysia and the revolving health care issues
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Increasing teen pregnancy cases are becoming a serious public health concern in both developing and developed nations for past decades. Teenage pregnancy occurs among adolescent girls between 10 and 19 years old. A recent study reveals that 14 out of every 1,000 female teenagers in Malaysia become pregnant every year. Such prevalence suggests there is still a lack of general understanding of reproductive health matters among the teenagers. The issue of teen pregnancy requires considerable attention to prevent more social and health problems such as more unintended pregnancies, baby dumping and extensive spread of sexually transmitted diseases within society.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Usability of ‘Rancanglah’ for health education in family planning: the perspective from healthcare personnel
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2023
Abstract: Advancement of digital technology brings great potential to complement current method in promoting family planning. Traditionally, health education on family planning is routinely delivered through face-to-face counseling during postnatal follow up at 6 weeks post-delivery. The innovation of RancangLah, a mobile-based application aims to educate women to choose the best family planning method for them apart from having awareness on their pregnancy risk.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utilization of private sector family planning services in Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/12/2020
Abstract: The private sector is playing an increasingly important role in family planning services globally. The active participation of private providers is associated with a higher contraceptive prevalence rate. The objectives is to examine the differentials and determinants of the utilizatio of private providers for family planning services. This study used the 2014 Malaysian Population and Family Survey Data. Cross-tabulations and logistic regression were performed on 1.817 current users of modern methods. Overall, 26% of modern method users obtained their supplies from private clinics/pharmacies and 15.2% from other sources, such as drug stores and sundry shops. The odds of obtaining supply from the private clinics/pharmacies were higher among the Chinese and urban women (AOR>1), and it was lower among those whose husbands decided on family planning had higher odds of obtaining the supply from the other sources (AOR>1). Conclusions, the private sector complements and supplements the public sector in providing family planning services to the public.
|
|
|
|
|
|
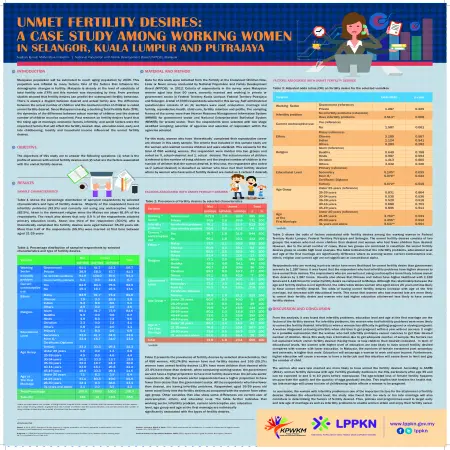
Unmet fertility desires: a case study among working women in Selangor, Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia population will be estimated to reach aging population by 2035. This projection was inflated by many factors. One of the factors that influence the demographic changes is fertility. Malaysia is already at the level of substitute of total fertility rate (TFR) and this number was decreasing by time. From previous studies showed that fertility desires can predict the subsequent fertility behavior. There is always a disjoint between desired and actual family size. The difference between the actual number of children and the desired number of children is called unmet fertility desired. Since Malaysia is having a declining Total Fertility Rate (TFR), the dynamics of the difference between actual number of children and the desired number of children must be examined. Past research on fertility desires found that the rising age at marriage, economic factors, infertility, and social factors were the important factors that will affect the fertility desired. Also, education level, early and late childbearing, locality and household income influenced the unmet fertility desires.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Universal health coverage in Malaysia: issues and challenges
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2014
Abstract: Socioeconomic development in Malaysia, over the past few decades, has led to the improvement and expansion of the public healthcare system. This system has provided universal access to a low-priced package of comprehensive health care leading Malaysia to claim to have achieved universal health coverage (UHC). However, the Malaysian health landscape is changing rapidly. Provision of private care has grown especially in large urban towns, mainly in response to public demand. Thus far, private care has been predominantly bought and utilised by the rich but because of differentials in quality of care between the public and private sector, unabated expansion of the private health sector has the potential to adversely affect universal access to care. This effect may be accentuated in the coming years by demographic changes in the country specifically by the ageing of the population. This paper is intended to highlight challenges to UHC in Malaysia in the face of the changing health landscape in the country and to offer some suggestions as to how these challenges can be met.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Understanding coping and resilience of children and adolescents
Item Type: Conference or Workshop Item
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2009
Abstract: The objectives of this paper are to identify and define key concepts and models related to stress, coping, and resilience amongst children and adolescents and also to make us mindful to area wise gaps in our evidence based practice in this context. Amidst the growing evidence that depression and other mental health issues are surfacing amongst children and adolescents in several societies, the author focuses on the transactional nature of coping and resilience and how children and adolescents process a variety of stresses that they see in their day to day lives. Given that children and adolescents attempt to cope well in stressful situations being a fact, the author considers constructing and reviewing this stressful experiences in a person-environment transaction context to be a useful strategy. The paper presents this strategy.
|
|
|
|