Browse by Type
|
|
Spirituality in parenting
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 01/10/2021
Abstract: The emergence of COVID-19 since last year has cause an unprecendented health crisis across the globe, affecting people physically, mentally, financially and socially. To alleviate the difficulties and stresses in dealing with the pandemic and ensuing lockdowns, multiple approaches have been taken by the governments, institutions and individuals. Spirituality plays a major role in helping some families cope during this extraordinary period. It can serve as an empowering foundation to any collective, the family unit being the most basic example. Indeed, spirituality is an integral component in parenting that should not be overlooked even during normal times.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correlates and consequences of delayed marriage in Malaysia
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 01/10/2021
Abstract: This paper aims to examine the correlates of age at first marriage and the consequences of late marriage. Data for this paper were drawn from the 2014 Malaysian Population and Family Survey. Simple cross- tabulation and multiple classification analysis were used for the analysis. Age at marriage of women varied across socioeconomic groups.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Penemuan tinjauan pendapat umum bersempena Sambutan Hari Bapa Peringkat Kebangsaan 2021 "Bapa Pemimpin Keluarga Sejahtera"
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2021
Abstract: The findings of an opinion survey conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (LPPKN) in conjunction with the National Father's Day 2021 celebration.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ordinal regression for modelling the family well- being among the Malaysians
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 30/06/2021
Abstract: Understanding factors which affect the level of family well-being is important as it contributes to effective decision making among the policymakers to improve the family lives as well as to strengthen the family institution. This study develops an ordinal regression model which identifies demographic, economic and social factors that are significant in explaining the status of family well-being.
|
|
|
|
|
|
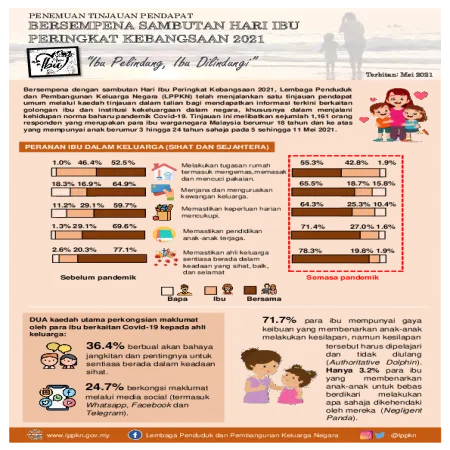
Penemuan tinjauan pendapat bersempena sambutan Hari Ibu Peringkat Kebangsaan 2021 "Ibu Pelindung, Ibu Dilindungi"
Item Type: Infographic
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2021
Abstract: In conjunction with the National Mother's Day 2021 celebration, LPPKN conducted a public opinion poll through online survey. The objective of this study is to obtain the latest information related to mothers and family institutions in the country, especially in living the new norms of the Covid-19 pandemic.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparison of rural and urban contraceptive methods preferences among married women in Malaysia, 2018
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 30/05/2021
Abstract: Contraceptive use among women remains an important public health intervention. Imperatively, the equality of family planning access between rural and urban areas allows all women to have the same opportunities to receive family planning service towards better well-being of families.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Determining important factors in Malaysian family well-being using tree-based classification techniques
Item Type: Book Section
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2021
Abstract: Tree-based classification techniques were used to identify the crucial factors influencing the Malaysian family well-being. Data from the nationwide survey, conducted by the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) of Malaysia in 2011 were used for the analysis. Two types of tree-based classification techniques, which are the decision tree and bagging decision tree, were considered for this study.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparison of rural and urban contraceptive methods preferences among married women in Malaysia, 2018
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 30/05/2021
Abstract: Contraceptive use among women remains an important public health intervention. Imperatively, the equality of family planning access between rural and urban areas allows all women to have the same opportunities to receive family planning services towards better well-being of families. The study aims at comparing the family planning preferences among women aged 15 to 49 throughout Malaysia in 2018 according to the geographical locations of rural ad urban areas. This is important for resources planning and allocation to the National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) clinic based on the locations. The data were collected from 49 NPFDB clinics throughout Malaysia. A total of 3668 married women aged 15 to 49 years used the family planning services in the NPFDB clinic in 2018. In this study, descriptive,. Chi-Square, and logistic regression analyses were carried out to compare the patterns and preferences of contraceptive use. The results analysis shows that the implant is the most popular method among all other contraceptive methods provided by the NPFDB clinics. Specifically, in both rural and urban areas, the three most popular contraceptive methods among married women in Malaysia in 2018 are implant, pill, and condom. Findings of the analysis based on the Chi-Square test show that age group, educations levels, and different types of contraception method were identified to have a significant association with the locations of either rural or urban areas. In conclusions, this study found that women who used implants as a method of contraceptives were often younger, better educated, and lived in an urban area. Therefore, the family planning providers especially NPFDB clinics play a key role in providing information, educating couples, and promoting the use of different family planning methods so that better family well-being could be achieved.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 54th session of the Commission on Population and Development: general debate on population, food security, nutrition and sustainable development
Item Type: Country Statement
Editor:
Year: 21/04/2021
Abstract: Malaysia’s population currently stands at 32,760,284 and is increasing at the rate of 0.6 percent per annum. Increased population increases food demand. Annually, Malaysia spends approximately USD8.33 billion (RM34.5 billion) on import of food supply, pointing to increased dependency food import purchases.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contraceptive use: patterns and preferences among new acceptors in Malaysia, 1990 to 2018.
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 05/04/2021
Abstract: Family planning is one of the important aspects in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG’s) in Goal 3 on Health and Goal 5 on Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment. Family planning is the basic need and women’s right to pregnancy, to get optimal health. The use of contraceptive enables women to attain their desired number of children and determine the gap of pregnancies towards the improvement of the families’ well-being of. The aim of this paper is to describe the patterns and preferences of contraceptive use among new acceptors attending a family planning clinic at National Population and Family Development Board (NPFDB) is sixteen states in Malaysia. The data analysis includes the new acceptors of contraception use among married women aged 15 to 49 years old, who attended a family planning clinic at NPFDB for the year 1990 to 2018. There are various types of contraceptive methods considered: contraceptive pills, Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUD), condom, hormone injection, implant, sterilization, rhythm and others. Results of the new acceptors at NPFDB clinic, with decreasing pattern from 1990 to 2018. While the use of implant, hormone injection and condom has increased steadily since 2004. The state of Perak has the highest number of new acceptors in most year, while the federal territory of Labuan has the lowest number of acceptors in most years within 29 years from 1990 to 2018. As a conclusion, this study has found that although the use of contraceptive pill is decreasing, it still becomes the most popular among a new acceptors in most of the states in Malaysia since 1990. However, the decreasing pattern of new acceptors for all types of contraceptive methods becomes our concern. Future research should therefore, concentrate on the investigation of the reduction number of new acceptors at NPFDB clinic. This is important to make sure the demands of contraceptive can be met and NPFDB clinics could provide better services towards better quality of life and better families’ well-being.
|
|
|
|