Browse by Type
|
|
Toleh kiri dan toleh kanan
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/06/2015
Abstract: The aspect of safety in the family needs to be educated and made a daily practice and needs to be educated with patience without despair. There are some simple tips to practice in family safety such as don’t stop praying, keep dangerous and important equipment in a special place, safe zone to explore and consensus brings blessings.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Imbangi keluarga dan kerjaya
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2015
Abstract: Based on the Fourth Malaysian Population and Family Survey (MPFS-4), it was found that overall, mothers do more leisure activities with their children, especially children under seven years old. This study found that the percentage of parents who often spend special time with their children is higher among mothers (80.2%) than fathers (65.3%). However, the percentage of those who frequently took their children on outings was almost the same between mothers (52.2%) and fathers (52.4%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apa wanita perlu tahu: subur@tidak subur?
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/05/2015
Abstract: Fertility is the ability to conceive naturally. As a measure, fertility rate is the number of children born per individual, household or population. Fertility varies according to fertility, i.e. the potential to reproduce (which is influenced by gamete production, fertilization and the ability to conceive long enough). There are several types of ovulation disorders that are 35% of the cause of infertility in women, namely anovulation. Anovulation is a condition where no ovulation process occurs or the egg process is released from the ovaries, oligovulation is an irregular ovulation process that sometimes occurs, sometimes not and the anovulation cycle is a menstrual cycle in which no ovulation process occurs at the cycle.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selamatkah mainan anak anda?
Item Type: Article
Editor:
Year: 00/04/2015
Abstract: Children's toy can help the educational and developmental process of children at an early age. However, the selection of children's toys needs to be done wisely especially if it involves safety aspects. If parents do not carefully choose toys, it can invite danger to the safety of children. To ensure the safety of children and prevent accidents or unwanted incidents, some things that need to be considered include choosing toys according to the level of age suitability of children, toys not made of toxic materials, avoid toys that contain magnetic materials or batteries to little children and toys that have noise.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Portrait of 1Malaysia Family First (1MFF)
Item Type: Book
Editor:
Year: 00/01/2015
Abstract: The 1MFF movement is a national agenda to increase commitment and invite all levels of society to return to giving priority to the family institution in all efforts, planning and actions. It is hoped that the 1Malaysia Family First (1MFF) element will create a lasting bond of love in family and community institutions. The initiatives introduced under the 1MFF Movement are implemented based on the 3 thrusts outlined in the National Family Policy, namely to increase the commitment and social responsibility of all parties in implementing family -friendly policies and programs; review and ensure existing laws, policies and regulations prioritize the family perspective; and provide family services and facilities that are easily accessible and accessible to families.
|
|
|
|
|
|
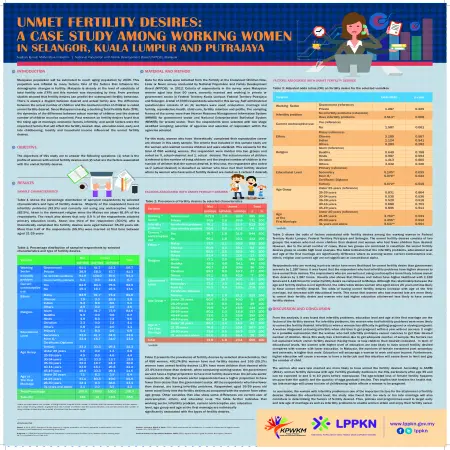
Unmet fertility desires: a case study among working women in Selangor, Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Malaysia population will be estimated to reach aging population by 2035. This projection was inflated by many factors. One of the factors that influence the demographic changes is fertility. Malaysia is already at the level of substitute of total fertility rate (TFR) and this number was decreasing by time. From previous studies showed that fertility desires can predict the subsequent fertility behavior. There is always a disjoint between desired and actual family size. The difference between the actual number of children and the desired number of children is called unmet fertility desired. Since Malaysia is having a declining Total Fertility Rate (TFR), the dynamics of the difference between actual number of children and the desired number of children must be examined. Past research on fertility desires found that the rising age at marriage, economic factors, infertility, and social factors were the important factors that will affect the fertility desired. Also, education level, early and late childbearing, locality and household income influenced the unmet fertility desires.
|
|
|
|
|
|
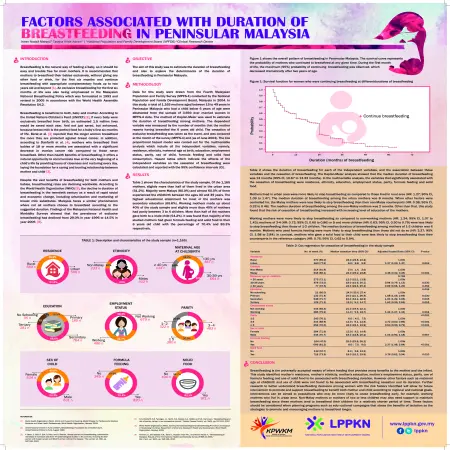
Factors associated with duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia
Item Type: Scientific Poster
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: Breastfeeding is the natural way of feeding a baby, so it should be easy and trouble free for most mothers. It is recommended that mothers to breastfeed their babies exclusively, without giving any other food or drink, for the first six months and continue breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods up to two years old and beyond [1]. An exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life was also being emphasized in the Malaysian National Breastfeeding Policy which was formulated in 1993 and revised in 2005 in accordance with the World Health Assembly Resolution 54.2. Breastfeeding is beneficial to both, baby and mother. According to the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) [2], if every baby were exclusively breastfed from birth, an estimated 1.5 million lives would be saved each year. And not just saved, but enhanced, because breast milk is the perfect food for a baby’s first six months of life. Beral et al. [3] reported that the longer women breastfeed the more they are protected against breast cancer. In addition, according to Danforth et al. [4], mothers who breastfeed their babies of 18 or more months are associated with a significant decrease in ovarian cancer risk compared to those never breastfeed. Other than health benefits of breastfeeding, it offers a natural opportunity to communicate love at the very beginning of a child’s life by providing hours of closeness and nurturing every day, laying the foundation for a caring and trusting relationship between mother and child [2]. Despite the vast benefits of breastfeeding for both mothers and babies, breastfeeding rates are declining worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [5], the decline in duration of breastfeeding in the twentieth century as a result of rapid social and economic change, including urbanization and marketing of breast milk substitutes. Malaysia faces a similar phenomenon where not all mothers choose to breastfeed according to the suggested duration. Findings of the Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Surveys showed that the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding had declined from 29.0 % in year 1996 to 14.5 % in year 2006 [6]. Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the duration of breastfeeding and also to explore the determinants of the duration of breastfeeding in Peninsular Malaysia.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sosialisasi dan kawalan sosial dalam kehidupan remaja berisiko: kajian kes di projek Perumahan Rakyat (PPR) Sri Pahang, Bangsar dan Sri Pantai, Lembah Pantai, Kuala Lumpur
Item Type: Thesis
Editor:
Year: 00/00/2015
Abstract: This study focused on a group of adolescents categorized as adolescents at risk in the People's Housing Project (PPR) area in urban areas. Purpose of the study is to identify and understand the life patterns of at -risk adolescents includes their involvement in deviant behavior, the role of socialization agents and forms of social control in the lives of at -risk adolescents. This study uses design qualitative form using in -depth interview and observation methods did not participate. A total of 10 teenagers consisted of six boys and four women aged between 16 to 22 years from PPR Sri Pahang, Bangsar and PPR Sri Pantai, Lembah Pantai have been purposefully selected.
|
|
|
|